Advertisements
Advertisements
Assertion: Recursion utilises more memory as compared to iteration.
Reason: Time complexity of recursion is higher due to the overhead of maintaining the function call stack.
Concept: Recursion
The following is a function of class Armstrong. This recursive function calculates and returns the sum of the cubes of all the digits of num, where num is an integer data member of the class Armstrong.
[A number is said to be Armstrong if the sum of the cubes of all its digits is equal to the original number].
There are some places in the code marked by ?1?, ?2?,?3? which may be replaced by a statement/expression so, that the function works properly.
public int sumOfPowers(int num)
{
if(num == 0)
return ?1?
int digit = ?2?;
return(int)Math.pow(digit, 3) + ?3?;
}
- What is the expression or statement at ?1?
- What is the expression or statement at ?2?
- What is the expression or statement at ?3?
Concept: Simple Recursive Functions (e.g. Factorial, GCD, Binary Search, Conversion of Representations of Numbers Between Different Bases)
A class LCM has been defined to find the Lowest Common Multiple of two integers.
Some of the data members and member functions are given below:
| Class name | LCM |
| Data members/instance variables: |
|
| n1 | to store an integer number |
| n2 | to store an integer number |
| large | integer to store the largest from n1,n2 |
| sm | integer to store the smallest from n1,n2 |
| l | to store lcm of two numbers |
| Methods / Member functions: | |
| LCM( ) | default constructor to initialize data members with legal initial values |
| void accept() | to accept n1 and n2 |
| int getLCM() | returns the lcm of n1 and n2 using the recursive technique |
| void display( ) | to print the numbers n1, n2 and lcm |
Specify the class LCM giving details of the constructor( ), void accept( ), int getLCM() and void display( ). Define a main ( ) function to create an object and call the member functions accordingly to enable the task.
Concept: Simple Recursive Functions (e.g. Factorial, GCD, Binary Search, Conversion of Representations of Numbers Between Different Bases)
The ability of an object to take many forms is known as ______.
Concept: Subclass Polymorphism and Dynamic Binding
A super class Godown has been defined to store the details of the stock of a retail store. Define a subclass Update to store the details of the items purchased with the new rate and update the stock. Some of the members of both the classes are given below:
| Class name | Godown |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| item | to store the name of the item |
| qty | to store the quantity of an item in stock |
| rate | to store the unit price of an item |
| amt | to store the net value of the item in stock |
| Member functions/methods: | |
| Godown(…) | parameterized constructor to assign value to the data members |
| void display( ) | to display the stock details |
| Class name | Update |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| pur_qty | to store the purchase quantity |
| pur_rate | to store the unit price of the purchased item |
| Member functions/methods: | |
| Update(…) | parameterized constructor to assign values to the data members of both the classes |
| void update( ) | to update the stock by adding the previous quantity by the purchased quantity and replace the rate of the item if there is a difference in the purchase rate. Also update the current stock value as: (quantity * unit price) |
| void display( ) | to display the stock details before and after updating |
Assume that the super class Godown has been defined. Using the concept of inheritance, specify the class Update giving details of the constructor, void update ( ) and void display( ).
The super class, main function and algorithm need NOT be written.
Concept: Member Access in Derived Classes
A super class EmpSal has been defined to store the details of an employee. Defie a subclass (overtime to compute the total salary of the employee, after adding the overtime amount based on the following criteria.
- If hours are more than 40, then 5000 are added to salary as an overtime amount
- If hours are between 30 and 40 (both inclusive), then 3000 are added to salary as an overtime amount
- If hours are less than 30, then the salary remains unchanged The details of the members of both the classes are given below:
| Class name | EmpSal |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| empnum | to store the name of the employee |
| empcode | integer to store the employee code |
| salary | to store the salary of the employee in decimal |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| EmpSal(...) | parameterised constructor to assign values to data members |
| void show() | to display the details of the employee |
| Class name | Overtime |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| hours | integer to store overtime in hours |
| totsal | to store the total salary in decimal |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| Overtime(....) | parameterised constructor to assign values to data members of both the classes |
| void calSal() | calculates the total salary by adding the overtime amount to salary as per the criteria given above |
| void show() | to display the employee details along with the total salary (salary +overtime amount) |
Assume that the super class EmpSal has been defined. Using the concept of inheritance, specify the class Overtime giving the details of the constructer (...), void calSal() and void show().
The super class, main function and algorithm need NOT be written.
Concept: Base and Derived Classes
The keyword used by a class to acquire the properties of an interface is:
Concept: Basic Data Structures (Stack, Queue, Dequeue)
State the principle by which the stack data structure works.
Concept: Basic Data Structures (Stack, Queue, Dequeue)
Convert the following infix notation to postfix notation:
A * (B + C / D ) – E / F Concept: Conversion of Infix to Prefix and Post Fix Notations
Answer the following question on the diagram of a Binary Tree given below:
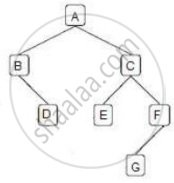
State the degree of the nodes C and G. Also, state the level of these nodes when the root is at level 0.
Concept: Recursive Data Structures - Single Linked List (Algorithm and Programming), Binary Trees, Tree Traversals (Conceptual)
Answer the following question on the diagram of a Binary Tree given below:

Write the pre-order and post-order traversal of the above tree structure.
Concept: Recursive Data Structures - Single Linked List (Algorithm and Programming), Binary Trees, Tree Traversals (Conceptual)
A Queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out).
Define a class Queue with the following details:
| Class name | Queue |
| Data member/instance variable: | |
| dat[ ] | array to hold the integer elements |
| cap | stores the maximum capacity of the queue |
| front | to point the index of the front |
| rear | to point the index of the rear |
| Member functions/methods: | |
| Queue(int max) | constructor to initialize the data member cap = max, front = rear = 0 and create the integer array |
| void add_dat(int v) | to add integers from the rear index if possible else display the message(“Queue full”) |
| int pop_dat( ) | to remove and return elements from front, if any, else returns -999 |
| void display() | to display elements of the queue |
Specify the class Queue giving the details of void add_dat(int) and int pop_dat( ). Assume that the other functions have been defined.
The main( ) function and algorithm need NOT be written.
Concept: Basic Data Structures (Stack, Queue, Dequeue)
What is the importance of the reference part in a Linked List?
Concept: Recursive Data Structures - Single Linked List (Algorithm and Programming), Binary Trees, Tree Traversals (Conceptual)
Convert the following infix notation to prefix notation.
(A - B)/C * (D + E)
Concept: Conversion of Infix to Prefix and Post Fix Notations
A double ended queue is a linear data structure which enables the user to add and remove integers from either ends i.e., from front or rear.
The details for the class deQueue are given below:
| Class name | deQueue |
|
Data members/instance variables: |
|
| Qrr[] | array to hold integer elements |
| lim | maximum capacity of the dequeue |
| front | to point the index of the front end |
| rear | to point the index of the rear end |
|
Methods/Member functions: |
|
| deQueue(int 1) | constructor to initialise lim = 1, front = 0 and rear =0 |
| void addFront(int v) | to add integers in the dequeue at the front end if possible, otherwise display the message “OVERFLOW FROM FRONT” |
| void addRear(int v) | to add integers in the dequeue at the rear end if possible, otherwise, display the message “OVERFLOW FROM REAR” |
| int popFront() | removes and returns the integers from the front end of the dequeue if any, else returns — 999 |
| int popRear ( ) | removes and returns the integers from the rear end of the dequeue if any, else returns — 999 |
| void show( ) | displays the elements of the dequeue |
Specify the class deQueue giving details of the function void addFront(int) and int popFront(). Assume that the other functions have been defined. The main() function and algorithm need NOT be written.
Concept: Basic Data Structures (Stack, Queue, Dequeue)
Differentiate between a stack and a queue.
Concept: Basic Data Structures (Stack, Queue, Dequeue)
Answer the following questions from the diagram of a Binary Tree given below:
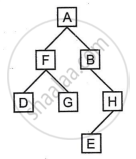
- Write the pre-order traversal of the above tree structure.
- Name the parent of the nodes D and B.
- State the level of nodes E anf F when the root is at level 0.
Concept: Recursive Data Structures - Single Linked List (Algorithm and Programming), Binary Trees, Tree Traversals (Conceptual)
Convert the following infix notation to postfix form.
(P + Q * R - S)/T * U
Concept: Conversion of Infix to Prefix and Post Fix Notations
CardGame is a game of mental skill, built on the simple premise of adding and removing the cards from the top of the card pile.
The details of the class CardGame are given below.
| Class name | CardGame |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| cards[] | array to store integers as cards |
| cap | to store the maximum capacity of array |
| top | to store the index of the topmost element of the array |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| CardGame(int cc) | constructor to initialise cap=cc and top= -1 |
| void addCard(int v) | to add the card at the top index if possible, otherwise display the message “CARD PILE IS FULL” |
| int drawCard( ) | to remove and return the card from the top index of the card pile, if any, else return the value -9999 |
| void display( ) | to display all the cards of card pile |
- Specify the class CardGame giving details of the functions void addCard(int) and int drawCard( ). Assume that the other functions have been defined.
The main() function and algorithm need NOT be written. - Name the entity described above and state its principle.
Concept: Implementation Directly Through Classes
Answer the following questions based on the diagram of a Binary Tree given below:
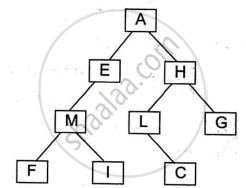
- Name the external nodes of the tree.
- State the degree of node M and node L.
- Write the post-order traversal of the above tree structure.
Concept: Recursive Data Structures - Single Linked List (Algorithm and Programming), Binary Trees, Tree Traversals (Conceptual)
