Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 from the given data
\[\ce{Ca_{(s)} + Cl2_{(g)} -> CaCl2_{(s)}}\] ∆`"H"_"f"^0` = − 795 kJ mol−1
Sublimation: \[\ce{Ca_{(s)} -> Ca-{(g)}}\] ∆`"H"_1^0` = + 121 kJ mol−1
Ionisation: \[\ce{Ca_{(g)} -> Ca^2+_{(g)} + 2e^-}\] ∆`"H"_2^0` = + 2422 kJ mol−1
Dissociation: \[\ce{Cl2_{(g)} -> 2Cl_{(g)}}\] ∆`"H"_3^0` = + 242.8 kJ mol−1
Electron affinity: \[\ce{Cl_{(g)} + e^- -> Cl^-_{(g)}}\] ∆`"H"_4^0` = −355 kJ mol−1
Solution
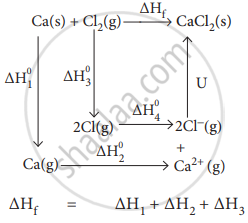
∆Hf = ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3 + 2∆H4 + u
− 795 = 121 + 2422 + 242.8 + (2 × − 355) + u
− 795 = 2785.8 – 710 + u
− 795 = 2075.8 + u
u = − 795 – 2075.8
u = −2870.8 KJ mol−1
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The bond dissociation energy of methane and ethane are 360 kJ mol–1 and 620 kJ mol–1 respectively. Then, the bond dissociation energy of the C-C bond is
What is lattice energy?
Write down the Born-Haber cycle for the formation of CaCl2
Suggest and explain an indirect method to calculate lattice enthalpy of sodium chloride crystal.
