Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Explain the types of price elasticity of demand.
Explain the price elasticity with its types.
Solution

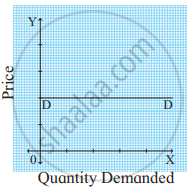
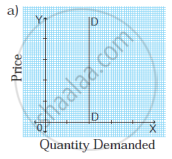
- Perfectly Elastic Demand (Ed = ∞): When a slight or zero change in the price brings about an infinite change in the quantity demanded of that commodity, it is called perfectly elastic demand. It is only a theoretical concept. For example, a 10% fall in price may lead to an infinite rise in demand.
Ed = `"Percentage change in Quantity Demanded"/"Percentage change in Price"` = ∞
Ed = ∞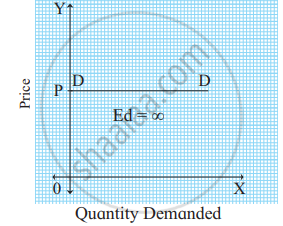
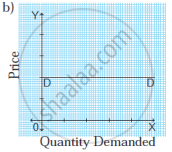
In the figure, the demand curve DD is a horizontal line parallel to the X-axis indicating perfectly elastic demand. - Perfectly inelastic demand (Ed = 0): When a percentage change in price has no effect on the quantity demanded of a commodity it is called perfectly inelastic demand. For example, a 20% fall in price will have no effect on the quantity demanded.
Ed = `(%Delta"Q")/(%Delta"P")`
Ed = `0/20 = 0`
Ed = 0
In practice, such a situation rarely occurs. For example, demand for salt, and milk.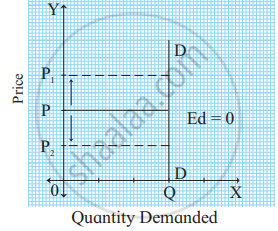
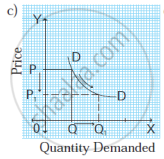
In the figure, when the price rises from OP to OP1 or when the price falls from OP to OP2, demand remains unchanged at OQ. Therefore, the demand curve is a vertical straight line parallel to the Y axis, indicating perfectly inelastic demand. - Unitary elastic demand (Ed = 1): When a percentage change in price leads to a proportionate change in quantity demanded then demand is said to be unitary elastic. For example, a 50% fall in the price of a commodity leads to a 50% rise in the quantity demanded.
Ed = `(%Delta"Q")/(%Delta"P") = 50/50 = 1`
∴ Ed = 1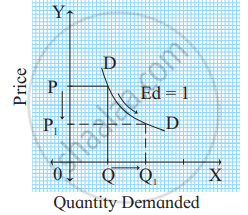
In the figure, when the price falls from OP to OP1 (50%), demand rises from OQ to OQ1 (50%). Therefore, the slope of the demand curve is a 'rectangular hyperbola'. - Relatively elastic demand (Ed >1): When a percentage change in price leads to more than proportionate change in quantity demanded, the demand is said to be relatively elastic. For example, a 50% fall in price leads to a 100% rise in quantity demanded.
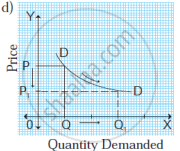
Ed = `(%Delta"Q")/(%Delta"P")`
Ed = `100/50`
∴ Ed = 2
Ed > 1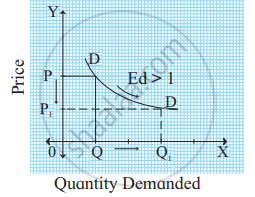
In the figure, when the price falls from OP to OP1 (50%), demand rises from OQ to OQ1 (100%). Therefore, the demand curve has a flatter slope. - Relatively inelastic demand (Ed < 1): When a percentage change in price leads to less than proportionate change in the quantity demanded, demand is said to be relatively inelastic. For example, a 50% fall in price leads to a 25% rise in quantity demanded.
Ed = `(%Delta"Q")/(%Delta"P") = 25/50 = 0.5`
Ed = 0.5
∴ Ed < 1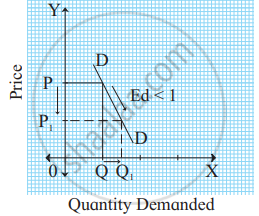
In the figure, when the price falls from OP to OP1 (50%), demand rises from OQ to OQ1 (25%). Therefore, the demand curve has a steeper slope.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Distinguish between Relatively elastic demand and relatively inelastic demand.
The demand curve is parallel to the X-axis in the case of ______.
When the percentage change in quantity demanded is more than the percentage change in price, the demand curve is ______.
Ed = 0 in case of ______.
Perfectly elastic demand : Ed = ∞ : : _______ : Ed = 0
Complete the correlation:
Rectangular hyperbola : ______ : Steeper demand curve : Relatively inelastic demand.
Assertion and Reasoning type of question:
- Assertion (A): The degree of price elasticity is less than one in case of relatively inelastic demand.
- Reasoning (R): The change in demand is less than the change in price.
In the following diagram, AE is the linear demand curve of a commodity. On the basis of the given diagram state whether the following statement is True or False. Give a reason for your answer.

Demand at point ‘B’ is unitary elastic demand.
In the following diagram, AE is the linear demand curve of a commodity. On the basis of the given diagram state whether the following statement is True or False. Give a reason for your answer.

Demand at point ‘D’ is perfectly inelastic demand.
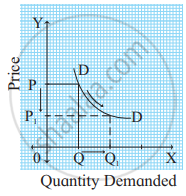
Identify and define the degrees of elasticity of demand from the following demand curve.

Identify and define the degrees of elasticity of demand from the following demand curve.
Identify and define the degrees of elasticity of demand from the following demand curve.
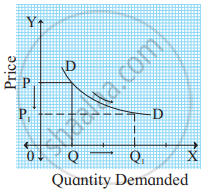
Identify and define the degree of elasticity of demand from the following demand curve.
Statements that are incorrect in relation to perfectly inelastic demand:
- Percentage change in price has no effect on quantity demanded
- Co-efficient of elasticity is equal to 1 (ed=1).
- Demand curve is a horizontal line parallel to X axis.
- It is a type of price elasticity of demand.
Relatively elastic demand : Ed > 1 :: Relatively inelastic demand : ______.
Infinite change in the quantity demanded of a commodity taking place due to slight or zero change in the price −
Demand curve is parallel to 'Y' axis in case of ______.
Assertion (A): The slope of demand curve is a rectangular hyperbola in case of unitary elastic demand.
Reasoning (R): In unitary elastic demand, percentage change in price leads to more than proportionate change in quantity demanded.
Identify & explain the concept from the given illustration
Kiran’s demand for milk remained unchanged even when its price increased by 10%.
Distinguish between perfectly elastic demand and perfectly inelastic demand.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Questions:
- Identify the types of price elasticity of demand from above diagram. (2m)
- Write slope of demand curve in above diagrams. (2m)
Complete the correlation.
Perfectly elastic demand : Ed = ∞ :: ______ : Ed = 1.
When the percentage change in quantity demanded is Less than the percentage change in price the demand curve is ______
Study the following figure and answer the question given below it.
Identify the price elasticity of demand from the following diagram:
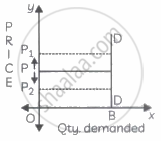
Study the following figure and answer the question given below it.
Identify the price elasticity of demand from the following diagram:
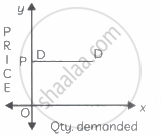
Study the following figure and answer the question given below it.
Identify the price elasticity of demand from the following diagram:
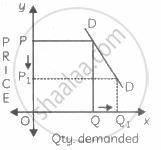
Study the following figure and answer the question given below it.
Identify the price elasticity of demand from the following diagram:
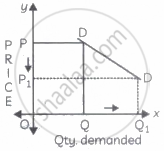
The price elasticity of demand on a linear demand curve at the Y-axis is equal to ______.
Distinguish between:
Unitary elastic demand and Relatively elastic demand
Study the following diagram and answer the questions:
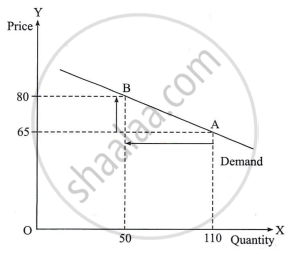
Questions:
- Calculate the price elasticity of demand using the ratio method.
- Find out the type of price elasticity of demand.
Complete the correlation:
Relatively inelastic demand : Perishable goods : : Relatively elastic demand : ______.
Identify and explain the concept from the given illustration:
A fall in the price of medicines by 30% resulted in no rise in demand for it.
Find the odd word out:
Types of price elasticity of demand:
Give an economic term:
Type of elasticity of demand having the value of elasticity of demand as one.
Find the odd word out:
Products having relatively inelastic demand:
Identify and explain the concept from the given illustration:
Demand for perfumes increased by 10% when its price decreased by 30%.
