Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How does the position of centromere form the basis of classification of chromosomes. Support your answer with a diagram showing the position of centromere on different types of chromosomes.
Solution
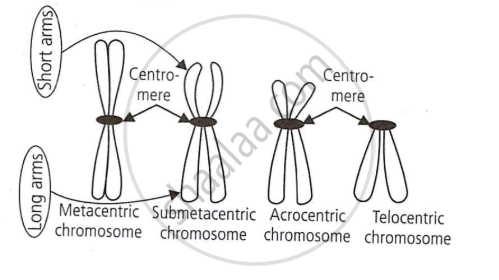
Another name for the centromere is main constriction. The kinetochore, a disc-shaped structure, is located on its side. Based on where the centromere is located on the chromosome, there are four different types of chromosomes.
- Metacentric chromosome: The centromere is located in the centre of this chromosome, and the lengths of the two arms are about equal.
- Submetacentric chromosome: One arm is marginally shorter than the other due to the centromere's modest distance from the centre point.
- Acrocentric chromosome: One arm is incredibly short and the other is incredibly long, and the centromere is located close to the end.
- Telocentric chromosome: The chromosome's apex is called the centromere. Humans do not have these chromosomes.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What are nuclear pores?
What is a centromere?
In a cell that is not dividing, the chromosomes are visible as a tangle of fine threads called
Chromosome having centromere in its middle is
When the centromere is situated in the middle of two equal arms of chromosomes, the chromosome is referred to as ______
Match List - I with List - II.
| List - I | List - II | ||
| (a) | Cristae | (i) | Primary constriction in chromosome |
| (b) | Thylakoids | (ii) | Disc-shaped sacs in Golgi apparatus |
| (c) | Centromere | (iii) | Infoldings in mitochondria |
| (d) | Cisternae | (iv) | Flattened membranous sacs in the stroma of plastids |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
A common characteristic feature of plant sieve tube cells and most of mammalian erythrocytes is ______.
What is the feature of a metacentric chromosome?
What is refer-ed to as satellite chromosome?
Discuss briefly the role of nucleolus in the cells actively involved in protein synthesis.
Write the function of the following:
Centromere
Explain the functions of the nuclear pores.
