Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are the steps involved in formation of a root nodule?
Solution 1
Nodule formation involves a sequence of multiple interactions between Rhizobium and roots of the host plant. Main stages in the nodule formation are:
(i) Rhizobia multiply and colonise the surrounding of roots and get attached to epidermal and root hair cells (Figure a).
(ii)The root hair curl and the bacteria invade the root hair.
(iii)An infection thread is produced carrying the bacteria into the inner cortex of the root (Figure b and c)
(iv)The bacteria get modified into rod-shaped bacteroids and cause inner cortical and pericycle cells to divide. Division and growth of cortical and peri cycle cells lead to nodule formation.
(v) The nodule thus formed, establishes a direct vascular connection with the host for exchange of nutrients (Figure d).
(vi)The nodule contains all the necessary biochemical components, such as the enzyme nitrogenase and leghaemoglobin. The enzyme nitrogenase catalyses the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia, the first stable product of nitrogen fixation.
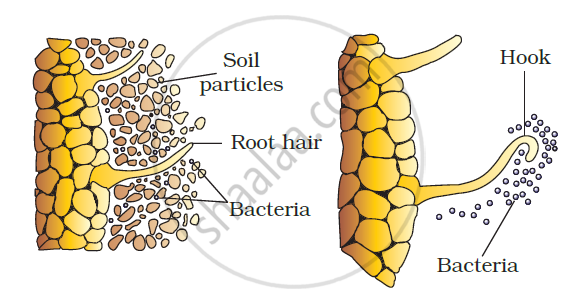
(a) (b)
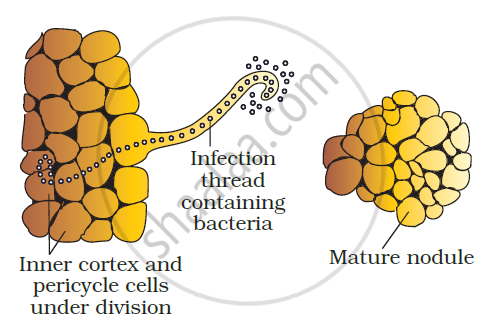
(c) (d)
Figure Development of root nodules
Solution 2
Multiple interactions are involved in the formation of root nodules. The Rhizobium bacteria divide and form colonies. These get attached to the root hairs and epidermal cells. The root hairs get curled and are invaded by the bacteria. This invasion is followed by the formation of an infection thread that carries the bacteria into the cortex of the root. The bacteria get modified into rod-shaped bacteroides. As a result, the cells in the cortex and pericycle undergo division, leading to the formation of root nodules. The nodules finally get connected with the vascular tissues of the roots for nutrient exchange.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What are the conditions necessary for fixation of atmospheric nitrogen by Rhizobium. What is their role in N2 -fixation?
Plants absorb nitrogen as ______.
In Glycine max, the product of biological nitrogen fixation is transported from the root nodules to other parts as ______.
In some plants, like soyabean, fixed nitrogen is exported into the transpiration stream as :
With regard to the Biological Nitrogen Fixation by Rhizobium in association with soybean, which one of the following statement/ statements does not hold true.
Nitrogen fixation is shown by prokaryotes and not by eukaryotes. Comment.
Name a plant which lacks chlorophyll. How will it obtain nutrition?
What is the function of leghaemoglobin in the root nodule of a legume?
Name one non-symbiotic nitrogen fixing prokaryote.
Rice fields produce an important greenhouse gas. Name it.
Name the most crucial enzyme found in root nodules for N2 fixation? Does it require a special pink coloured pigment for its functioning? Elaborate.
Trace the events starting from the coming in contact of Rhizobium to a leguminous root till nodule formation. Add a note on importance of leg hemoglobin
Give the biochemical events occurring in the root nodule of a pulse plant. What is the end product? What is its fate?
