Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is plasticity?
Solution
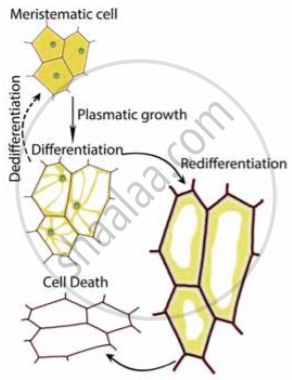
Plants follow different pathways in response to the environment or phases of life to form different kinds of structures. This ability is called plasticity,
eg: Heterophylly in cotton and coriander. In such plants, the leaves of the juvenile plant are different in shape from those in mature plants.
Sequences of developmental process in a plant cell
On the other hand, the difference in shapes of leaves produced in air and those produced in water in buttercup also represent the heterophyllous development due to the environment. This phenomenon of heterophylly is an example of plasticity.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Multiple Choice Question:
In guard cells, when sugar is converted into starch, the stomatal pore ______.
Multiple Choice Question:
Which of the following type of solution has a lower level of solutes than the solution?
Multiple Choice Question:
Water absorption takes place through ______.
Multiple Choice Question:
Due to low atmospheric pressure the rate of transpiration will ____________.
How phosphorylase enzyme open the stomata in starch sugar interconversion theory?
What are the parameters which control water potential?
List out the non-photosynthetic parts of a plant that need a supply of sucrose?
An artificial cell made of selectively permeable membrane immersed in a beaker (in the figure). Read the values and answer the following questions?

- Draw an arrow to indicate the direction of water movement.
- Is the solution outside the cell isotonic, hypotonic or hypertonic?
- Is the cell isotonic, hypotonic or hypertonic?
- Will the cell become more flaccid, more turgid or stay in its original size?
- With reference to the artificial cell state, is the process endosmosis or exosmosis? Give reasons.
When a cell is fully turgid which of the following will be zero?
What makes elixir of life it so important?
