Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With a neat, labelled diagram, describe the parts of a typical angiosperm ovule.
Solution
An ovule is a female megasporangium where the formation of megaspores takes place.

The various parts of an ovule are:
- Funiculus: It is a stalk-like structure which represents the point of attachment of the ovule to the placenta of the ovary.
- Hilum: It is the point where the body of the ovule is attached to the funiculus.
- Integuments: They are the outer layers surrounding the ovule that provide protection to the developing embryo.
- Micropyle: It is a narrow pore formed by the projection of integuments. It marks the point where the pollen tube enters the ovule at the time of fertilisation.
- Nucellus: It is a mass of the parenchymatous tissue surrounded by the integuments from the outside. The nucellus provides nutrition to the developing embryo. The embryo sac is located inside the nucellus.
- Chalazal: It is the basal, swollen part of the nucellus from where the integuments originate.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
With a neat diagram explain the 7-celled, 8-nucleate nature of the female gametophyte.
Where exactly is the filiform apparatus present in the embryo sac of an angiosperm? States its function.
Give a scientific term for the following:
Entry of pollen tube into an ovule through integuments.
Answer the following question.
Draw the diagram of a pistil where pollination has successfully occurred. Label the parts involved in reaching the male gametes to its desired destination.
Describe the process of megasporogenesis up to fully developed embryo sac formation in an angiosperm.
Given below is the diagram of a human ovum surrounded by a few sperms. Study the diagram and answer the following questions :
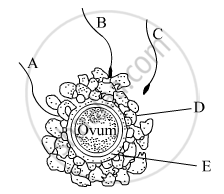
(a) Which one of the sperms would reach the ovum earlier?
(b) Identify 'D' and 'E'. Mention the role of 'E'.
(c) Mention what helps the entry of sperm into the ovum and write the changes occurring in the ovum during the process.
(d) Name the specific region in the female reproductive system where the event represented in the diagram takes place.
Egg apparatus consists of ______.
Embryo sac is also known as ______.
Embryo sac is found in ______.
Entry of pollen tube through micropyle is ______.
Ovule is straight with funiculus, embryo sac, chalaza, and micropyle lying on one straight line. It is ______.
Eight nucleate embryo sacs are ______.
What is the direction of micropyle in anatropous ovule?
An ovule which becomes curved so that the nucellus and embryo sac lie at right angles to the funicle is ______.
Polygonum type of embryo sac is ______.
An embryo may sometimes develop from any cell of embryo sac other than egg. It is termed as ______.
The hilum is a scar on the:
Megasporangium is equivalent to ______.
Which one of the following pairs of plant structures has a haploid number of chromosomes?
