Topics
Computer System
- Computer System
- History of Computers
- Types of Computer Memory
- Memory Unit (Memory Devices)
- Data Transfer Between Memory and CPU
- Basics of Microprocessors
- Microprocessor Specifications
- Introduction to Microcontroller
- Introduction to Microcontroller
- Data and Information
- Data Types
- Data Capturing, Storage and Retrieval
- Data Deletion and Recovery
- Software
- System Software and Its Types
- Programming Tools of System Software
- Application Software
- Proprietary Or Free and Open Source Software
- Introduction to Operating System (OS)
- OS User Interface and Its Types
- Functions of Operating System
Encoding Schemes and Number System
- Encoding Schemes and Number System
- American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII)
- Indian Script Code for Information Interchange (ISCII)
- UNICODE
- Introduction to Number Systems
- The Decimal Number System
- Binary Number System
- Octal Number System
- Hexadecimal Number System
- Number System Conversions
- Conversion from Decimal to Other Number Systems
- Conversion from Other Number Systems to Decimal Number System
- Conversion from Binary Number to Octal/Hexadecimal Number and Vice-versa
- Conversion of a Number with Fractional Part
Emerging Trends
- Concept of Emerging Trends
- AI (Artificial Intelligence)
- Machine Learning
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Immersive Experiences
- Robotics
- Big Data
- Characteristics of Big Data
- Data Analytics
- IoT (Internet of Things)
- Web of Things (WoT)
- Sensors
- Concept of Smart Cities
- Cloud Computing
- Cloud Services
- Grid Computing
- Blockchains
Introduction to Problem Solving
- Problem Solving
- Steps for Problem Solving
- Algorithms
- Why Do We Need an Algorithm?
- Representation of Algorithms
- Flowchart
- Pseudocode
- Introduction to Flow of Control
- Sequence
- Selection
- Repetition
- Verifying Algorithms
- Comparison of Algorithm
- Coding
- Decomposition
Getting Started with Python
- Introduction to Python
- Key Features of Python
- Working with Python
- Execution Modes
- Python Keywords
- Identifiers
- Variables
- Comments
- Everything is an Object
- Python Data Types
- Number
- Sequence
- Set
- None
- Mapping
- Classification of Data Types
- Deciding Usage of Python Data Types
- Operators in Python
- Operators - Arithmetic Operators (-,+,*,/,%)
- Relational Operator (>,>=,<=,=,!=)
- Assignment Operators
- Logical Operators (!,&&,||)
- Identity Operators
- Membership Operators
- Expressions
- Statement
- Input and Output
- Type Conversion
- Explicit Conversion
- Implicit Conversion
- Debugging
Flow of Control
- Flow of Control
- Selection
- Indentation
- Repetition
- The ‘For’ Loop
- The ‘While’ Loop
- Types of Statements in Loop
- Break Statement
- Continue Statement
- Nested Loops
Functions
- Introduction to Functions
- Functions
- The Advantages of Function
- User Defined Functions
- Creating User Defined Function
- Arguments and Parameters
- Functions Returning Value
- Flow of Execution
- Scope of a Variable
- Python Standard Library
- Built-in Functions
- Module
- Types of Module
- Built-in Modules
- From Statement
Strings
- Introduction to Strings
- String
- String Operators
- Traversing a String
- Built-in String Functions
- String Handling
Lists
- List
- List Operations
- Traversing a List
- List Methods and Built-in Functions
- Nested Lists
- Copying Lists
- List as Argument to a Function
- List Manipulation
Tuples and Dictionaries
- Tuples
- Tuple Operations
- Tuple Methods and Built-in Functions
- Tuple Assignment
- Nested Tuples
- Tuple Handling
- Introduction to Dictionaries
- Dictionaries Are Mutable
- Dictionary Operations
- Traversing a Dictionary
- Dictionary Methods and Built-in Functions
- Manipulating Dictionaries
Societal Impact
- Digital Technologies
- Digital Footprints
- Digital Society and Netizen
- Data Protection
- Intellectual Property Right
- Software Licensing
- Violation of Intellectual Property Right (IPR)
- Public Access and Open Source Software
- Cyber Crimes
- Indian Information Technology Act (IT Act)
- Impact on Health
The Decimal Number System
A decimal number is a fraction whose denominator can be expressed as 10 or some higher power of 10. The dot represents a decimal point. For example, 2.53, 6.5, etc.
Representation of Decimal Numbers:
- When there is no number to the left of the decimal point, generally, a zero is written.
i.e., .72 is written as 0.72 - 2.4 means 2 + 0.4.
Here, 2 is the integral part, and 0.4 is the decimal part of the number 2.4. - Any extra zero or zeroes written after the decimal part of a number do not change its value.
e.g., a value of 3.5 is the same as 3.50, 3.500, or 3.5000, and so on. - The decimal point is used to write 8 `5/10` as 8.5. This is read as ‘eight point five.'
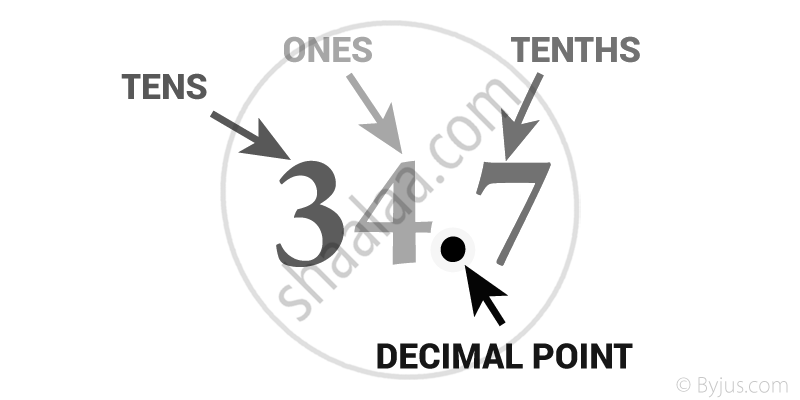
- In a decimal number, the digits to the left of the decimal point represent a whole number. The digits to the right of the decimal represent the parts. The place value of the digits becomes 10 times smaller.
- 34.7 has 3 Tens, 4 Ones, and 7 Tenths
Example
Write the following as decimals: Two ones and five-tenths
Two ones and five-tenths = 2 + `5/10` = 2.5.
Example
Write the following as decimals: Thirty and one-tenth
Thirty and one-tenth = 30 + `1/10` = 30.1
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Shaalaa.com | Introduction To Decimals Part-1
to track your progress
Series: Concept of Decimals Numbers
0%
