Topics
Elementary Theory of Demand
- Concept for Demand
- Types of Demand
- Demand Schedule
- Demand Curve
- Determinants of Demand Or Demand Function
- Law of Demand
- Assumptions of Law of Demand
- Exceptions to the Law of Demand
- Movement Along and Shifts in the Demand Curve
- Shift in Demand Curve
Demand and Supply: Basic Concepts
Factors of Production: Basic Concepts
Elasticity of Demand
Theory of Supply
- Concept of Supply
- Difference Between Supply and Stock
- Types of Supply
- Determinants Or Factors Governing the Supply
- Supply Function
- Supply Schedule
- Supply Curve
- Law of Supply
- Assumptions of the Law of Supply
- Exceptions to the Law of Supply
- Why Does the Supply Curve Slopes Upward to the Right
- Movement Along the Supply Curve and Shift in Supply Curve
- Movement Along the Supply Curve: Variations (Extension Or Contraction) of Supply
- Shift in Supply Curves
- Distinction Between Change in Quantity Supplied (Or Movement Along Supply Curve and Change in Supply Or Shift of the Supply Curve)
- Distinction Between Expansion in Supply and Increase in Supply
- Distinction Between Contraction in Supply and Decrease in Supply
- Elasticity of Supply
Alternative Market Structures: Basic Concepts
Elasticity of Supply
- Elasticity of Supply
- Degrees of Elasticity of Supply
- Measurement of Elasticity of Supply
- Factors Affecting Elasticity of Supply
The State and Economic Development
Factors of Production
- Production is Transformation
- Meaning of Production Mechanism
- Factors of Production
- Factors of Production - Land
- Factors of Production: Labour
- Factors of Production: Capital
- Factors of Production Entrepreneur
- Relative Importance of Different Factors of Production
Money and Banking: Basic Concepts
Land
- Land
- Characteristics of Land
- Functions of Land
- Importance of Land
- Productivity of Land
- Factors Affecting Productivity of Land
Destruction of Ecosystem
- Ecosystem
- Industrialisation
- Urbanisation
- Migration
- Dwelling Units
- Mining
- Construction of Dams
- Shifting Cultivation
- Causes of Destruction of Ecosystem
Labour
- Factors of Production: Labour
- Characteristics of Labour
- Labour: an Important Factor of Production
- Entrepreneur - Special Type of Labour
- Labour and Economic Activities
- Division (Specialisation) of Labour
- Types of Division of Labour
- Advantages of Division of Labour
- Disadvantages of Division of Labour
- Necessary Conditions for the Division of Labour
- Efficiency of Labour
- Reasons for Low Efficiency of Labour in India
- Suggestions for Improving the Efficiency of Indian Workers
Capital and Capital Formation
- Factors of Production: Capital
- Difference Between Capital and Other Related Concepts
- Differences Between Land and Capital
- Differences Between Capital and Labour
- Characteristics of Capital
- Types of Capital
- Functions of Capital
- Capital Formation
- Is Land Capital?
- Factors Influencing Or Affecting Capital Formation
- Significance of Capital Formation
- Causes of Low Rate of Capital Formation
- Suggestions to Raise Rate of Capital Formation
Entrepreneur
- Factors of Production Entrepreneur
- Functions of an Entrepreneur
- Difference Between Entrepreneur and Organisation
- Distinction Between Labour and Entrepreneur
- Distinction Between Capitalist and Entrepreneur
- Qualities to Be a Successful Entrepreneur
- Role of Entrepreneurs in Economic Development
Nature and Structure of Markets
- Alternative Market Structures
- Concept of Market
- Characteristics of Market
- Forms of Market Structure
- Factors Determining Forms of Market
- Market Structures
- Extent of Market
- Similarities Between Monopolistic Competition and Perfect Competition
- Similarities Between Monopolistic Competition and Monopoly
The State and Economic Development
- The State and Economic Development
- Introduction of Public and Private Sector
- Functions of the State in Promoting Economic Development
- Role of State in Economic Development
Instruments of State Intervention
- The Instruments of State Intervention
- Meaning of Fiscal Policy
- Objectives of Fiscal Policy
- Instruments of Fiscal Policy
- Types of Taxes
- Monetary Policy
- Distinction Between Monetary and Fiscal Policy
Public Sector Enterprises
- Public Sector Enterprises
- Role of Public Sector Enterprises
- Problems of Public Sector Enterprises/Reasons for Declining Popularity of Public Sector
- Suggestions to Improve the Efficiency of Public Sector Enterprises
Privatization of Public Enterprises
- Privatization of Public Enterprises
- Need for Privatisation
- Rationale of Privatisation in India
- Reasons in Favour of Privatisation
- Pre-requisites for Privatisation
- Limitations of the Privatisation
- Suggestive Framework for Privatisation
- Arguments for Privatisation Or Disinvestment
- Arguments Against Privatisation (Or Disinvestment)
- Privatisation in India
Money and Inflation
- Money
- Concept for Barter System
- Inconveniences Or Difficulties of Barter System
- Functions of Money
- Importance of Money
- Types of Money
- Forms of Money
- Features of Money
- Introduction of Inflation
- Characteristics of Inflation
- Types of Inflation
- Causes of Inflation
- Effects of Inflation
- Anti-inflationary Measures
Banking : Commercial Banks and Central Bank
- Meaning of Commercial Banks
- Importance of Banks
- Commercial Banks: Functions
- Money Creation Or Credit Creation by the Commercial Banking System
- Nationalisation of Banks
- Meaning of Central Bank
- Differences Between a Central Bank and a Commercial Bank
- Need for a Central Bank
- Functions of a Central Bank
- Monetary Policy of the Central Bank
- Various Aspects of Credit Control Measures
- Objectives of Credit Control
- Method of Credit Control - Qualitative
- Method of Credit Control - Quantitative
- Reserve Bank of India
Land:
Land is made up of stones, soil, and large rocks, but it isn’t the same everywhere. In some areas, it is flat, while in others it is hilly. All land-dwelling animals, including humans, live on land. Some animals dig burrows into the ground for shelter, using the land for their needs. People also rely on land for farming, building houses, and constructing roads. Additionally, plants and animals in forests that grow on land are used for various purposes.
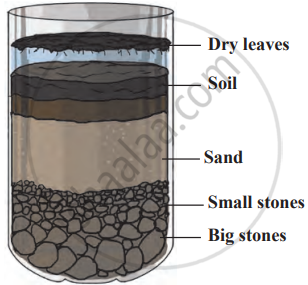
Layers of the mixture in the bottle
- Land provides valuable resources like minerals, crude oil, and natural gas, making it an important resource for human life.
- To understand what land is made of, one can observe the layers of soil and rock when pits are dug, such as when a pipeline is being laid.
- Decomposing dead plants and animals results in the formation of humus, the top layer of mature soil. This layer is most commonly found in dense forests.
- Beneath this, the land contains sand, small stones, soil, and living creatures like worms and insects. Below this layer lies immature soil, along with pieces of bedrock.
- As one digs deeper, the amount of soil decreases, and more rock appears. This bottom layer is called bedrock, and it is from these rocks that the minerals in the soil come.
- Because of this, the soil in different regions can vary in colour and texture, depending on the type of bedrock underneath.
Humus (Top Layer)
↓
Soil and Stones
↓
Bedrock and Soil
↓
Bedrock (Bottom Layer)
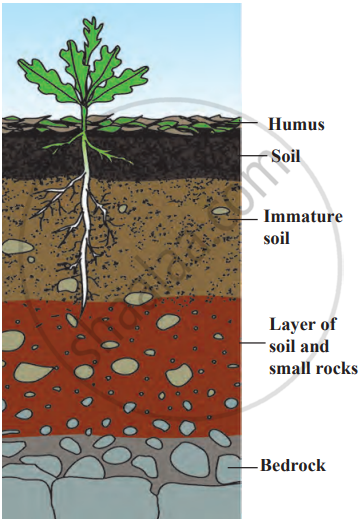
Layers of land
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
