Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A 0.05 M NH4OH solution offers the resistance of 30.8 ohms to a conductivity cell at 298K. If the cell constant is 0.343 cm−1 and the molar conductance of NH4OH at infinite dilution is 471.4 S cm2 mol−1, calculate the following:
- Specific conductance
- Molar conductance
- Degree of dissociation
उत्तर
Given:
Molarity (M) = 0.05 M
Resistance = 30.8 Ω
Cell constant = 0.343 cm−1
Molar conductance `π_(m)^∞` = 471.4 s cm2 mol−1
(1) Specific conductance (K)
= `1/"R" xx "cell constant"`
= `1/30.8 xx 0.343`
= 0.011Ω−1 cm−1
(2) Molar conductance (πm)
`π = ("K" xx 1000)/"M"`
= `(0.011 xx 1000)/0.05`
= 220 Ω−1 cm2/mol
(3) Degree of dissociation (α)
`α = (π_m)/(π_(m)^∞)`
= `220/471.4`
= 0.47
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
The unit of conductance is ………. and that of specific conductance is ………..
(Henry’s, aldol condensation, absence, do not, ohm, Raoult’s, increases, common ion effect, easily, three, solubility product, ohm-1, two, four, ohm-1, cm2, Cannizzaro, ohm-1 cm-1, zero, decreases, presence)
A 0.05 M NH4OH solution offers the resistance of 50 ohms to a conductivity cell at 298 K. If the cell constant is 0.50 cm-1 and molar conductance of NH4OH at infinite dilution is 471.4 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1, calculate:
(i) Specific conductance
(ii) Molar conductance
(iii) Degree of dissociation
The molar conductance of a solution _______ with dilution, while its specific conductance _______ with dilution.
In the diagram of the electrolytic cell given below, A, B and C are connected in series having electrolytes of ZnSO4, AgNO3 and CuSO4, respectively.
A steady current of 1.5 A was passed until 1.45 g of Ag was deposited at the cathode of cell B.
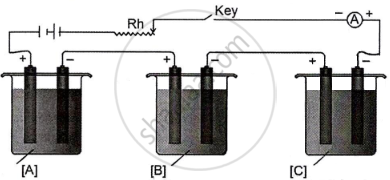
(Atomic mass of Ag = 108, Cu = 63.5, Zn = 65.3)
Answer the following questions:
- How long did the current flow?
- What weight of Cu and Zn was deposited at the cathode?
