Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A 50 cm long solenoid has 400 turns per cm. The diameter of the solenoid is 0.04 m. Find the magnetic flux linked with each turn when it carries a current of 1 A.
उत्तर
Length of the solenoid, l = 50 cm = 50 × 10-2 m
No. of turns/cm = 400
For 50 cm, No. of turns N = 400 × 50 = 20,000
Diameter of the solenoid = 0.04 m
∴ Radius of the solenoid = 0.02 m
Current passing through the solenoid = 1 A
Area of the solenoid = πr²
= 3.14 × 0.02 × 0.02 m2
Formula :-
Magnetic flux, φ = µ0 n2 AIl
n = `"N"/l`
`therefore φ = (mu_0 "N"^2 "AI")/l`
`φ = (4 xx 3.14 xx 10^-7 xx 20,000 xx 20,000 xx 3.14 xx 0.02 x 0.02 xx 1)/(50 xx 10^-2)`
`= (6310144 xx 10^-7)/(50 xx 10^-2)`
`= 126202.88 xx 10^-7 xx 10^2`
= 126202.88 × 10-5
φ = 1.262 Wb
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Describe different ways to induce current in a coil of wire.
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
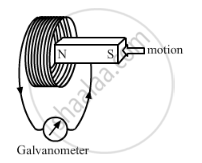
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
Fig. shows a simple form of an A.C. generator.

(a) Name the parts labeled A and B.
(b) What would be the effect of doubling the number of turns on the coil if the speed of rotation remains unchanged?
(c) Which of the output terminals is positive if the coil is rotating in the
direction shown in the diagram (anticlockwise)?
( d ) What is the position of the rotating coil when p.d. across its ends is zero? Explain why p.d. is zero when the coil is at this position .
(e) Sketch a graph showing how the p.d. across the ends of the rotating coil varies with time for an A.C. dynamo.
( f) On th e same sheet of paper and vertically below the first graph using the same time scale, sketch graphs to show the effect of
(i) Doubling the speed of rotation and at the same time keeping
the field and the number of turns constant,
(ii ) Doubling the number of turns on the coil and at the same time
doubling the speed of rotation of the coil, keeping th e speed
constant.
List some of the practical applications of an electromagnet.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then ______.
