Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A concave lens has focal length 15 cm. At what distance should the object from the lens be placed so that it forms an image at 10 cm from the lens? Also find the magnification produced by the lens.
उत्तर
Focal length of concave lens f = - 15 cm
Image distance v = - 10 cm ( image formed by a concave lens is on the left side of the lens)
Using the lens formula:
`1/f=1/v-1/u`
`1/-15=1/-10-1/u`
`1/u=1/15-1/10`
`1/u=(2-3)/30=-1/30`
∴ u = - 30 cm.
The object is at a distance of 30 cm from the lens and on its left.
The magnification of the concave lens is given as:
Magnification = `"image distaance"/"object distance"`
`m=v/u=(-10)/-30=1/3`
Since the magnification is less than 1, the image is smaller than the object.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Where must the object be placed for the image formed by a converging lens to be:
real, inverted and smaller than the object?
An illuminated object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a converging lens of focal length 15 cm. The image obtained on the screen is:
(a) upright and magnified
(b) inverted and magnified
(c) inverted and diminished
(d) upright and diminished
Construct ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of a virtual image using a diverging lens.
A person cannot see distant objects clearly. His vision can be corrected by using the spectacles containing:
(a) concave lenses
(b) plane lenses
(c) contact lenses
(d) convex lenses
The following diagram in given below shows an object OA and its virtual image IB formed by a lens.
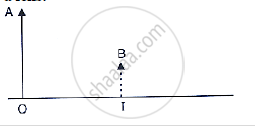
A lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object irrespective of its position. What kind of lens is this?
An object of height 4 cm is kept at a distance of 30 cm from a concave lens. Use lens formula to determine the image distance, nature and size of the image formed if focal length of the lens is 15 cm.
When an object is kept within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image is formed behind the mirror. This image is :
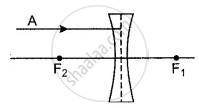
In figure give below of thin concave lens, F1 and F2 are its foci, complete the path of the given ray of light after it emerges out of the lens.
Draw images in case of a concave lens when the object is at infinity.
