Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A current of 1.6 mA flows through a conductor. If charge on an electron is –1.6 × 10-19 coulomb, find the number of electrons that will pass each second through the cross section of that conductor.
उत्तर
Current, I = 1.6 mA = 1.6 × 10-3 A
Charge, Q = -1.6 × 10-19 coulomb
t = 1 sec
Charge flowing through the conductor in one second
I = `"Q"/"t"`
Q = I × t
Substituting the values in the formula above we get,
Q = 1.6 × 10-3 × 1
= 1.6 × 10-3
No. of electrons = `(1.6 xx10^-3)/(1.6xx10^-19)`
= `10^16`
Therefore, the number of electrons that will pass each second through the cross section of that conductor = 1016
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the SI unit of potential difference?
Name a device which helps to maintain potential difference across a conductor (say, a bulb).
If a potential difference of 10 V causes a current of 2 A to flow for 1 minute, how much energy is transferred?
What p.d. is needed to send a current of 6 A through an electrical appliance having a resistance of 40 Ω?
How is the electric potential difference between the two points defined? State its S.I. unit.
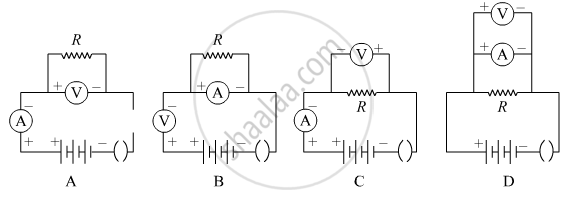
Which one of the following is the correct set-up for studying the dependence of the current on the potential difference across a resistor and why?
In the figure given below, A, B and C are three ammeters. The ammeter B reads 0.5A. (All the ammeters have negligible resistance.)
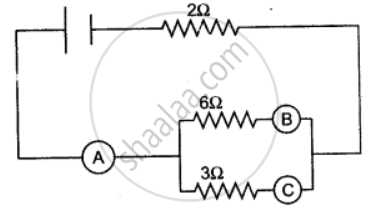
Calculate:
(i) the readings in the ammeters A and C.
(ii) the total resistance of the circuit.
100 J of heat is produced each second in a 4 Ω resistor. The potential difference across the resistor will be:
What does the positive and negative sign of potential convey?
