Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
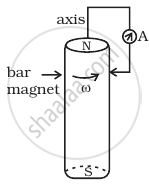
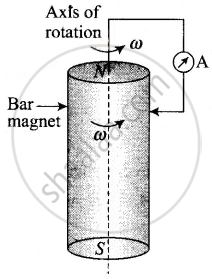
A cylindrical bar magnet is rotated about its axis (Figure). A wire is connected from the axis and is made to touch the cylindrical surface through a contact. Then
विकल्प
a direct current flows in the ammeter A.
no current flows through the ammeter A.
an alternating sinusoidal current flows through the ammeter A with a time period T = 2π/ω.
a time varying non-sinosoidal current flows through the ammeter A.
उत्तर
A cylindrical bar magnet is rotated about its axis (Figure). A wire is connected from the axis and is made to touch the cylindrical surface through a contact. Then no current flows through the ammeter A.
Explanation:
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is used in this problem. Whenever the number of magnetic lines of force (magnetic flux) passing through a circuit changes (or a moving conductor cuts the magnetic flux) an emf is produced in the circuit (or emf induces across the ends of the conductor) is called induced emf. The induced emf persists only as long as there is a change or cutting of flux.
When cylindrical bar magnet is rotated about its axis, no change in flux linked with the circuit takes place, consequently no emf is induced and hence, no current flows through the ammeter A. Hence the ammeter shows no deflection.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate magnetic flux density of the magnetic field at the centre of a circular coil of 50 turns, having a radius of 0.5m and carrying a current of 5 A.
Answer the following question.
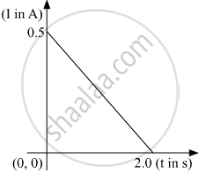
When a conducting loop of resistance 10 Ω and area 10 cm2 is removed from an external magnetic field acting normally, the variation of induced current-I in the loop with time t is as shown in the figure.
Find the
(a) total charge passed through the loop.
(b) change in magnetic flux through the loop
(c) magnitude of the field applied
Two inductors of inductance L each are connected in series with the opposite? magnetic fluxes. The resultant inductance is ______.
The unit of magnetic flux in SI is ______
The dimensional formula of magnetic flux is ______.
A square of side L meters lies in the x-y plane in a region, where the magnetic field is given by `B = Bo(2hati + 3hatj + 4hatk)`T, where B0 is constant. The magnitude of flux passing through the square is ______.
A loop, made of straight edges has six corners at A(0, 0, 0), B(L, O, 0) C(L, L, 0), D(0, L, 0) E(0, L, L) and F(0, 0, L). A magnetic field `B = B_o(hati + hatk)`T is present in the region. The flux passing through the loop ABCDEFA (in that order) is ______.
A coil is placed in a time varying magnetic field. If the number of turns in the coil were to be halved and the radius of wire doubled, the electrical power dissipated due to the current induced in the coil would be: (Assume the coil to be short circuited.)
The Figure below shows an infinitely long metallic wire YY' which is carrying a current I'.
P is a point at a perpendicular distance r from it.
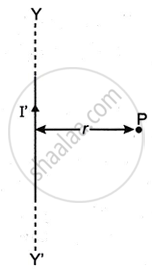
- What is the direction of magnetic flux density B of the magnetic field at the point P?
- What is the magnitude of magnetic flux density B of the magnetic field at the point P?
- Another metallic wire MN having length l and carrying a current I is now kept at point P. If the two wires are in vacuum and parallel to each other, how much force acts on the wire MN due to the current I' flowing in the wire YY'?
