Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A diploid organism is heterozygous for 4 loci, how many types of gametes can be produced?
उत्तर
Locus is a fixed position on a chromosome, which is occupied by a single or more genes. Heterozygous organisms contain different alleles for an allelic pair. Hence, a diploid organism, which is heterozygous at four loci, will have four different contrasting characters at four different loci.
For example, if an organism is heterozygous at four loci with four characters, say Aa, Bb, Cc, Dd, then during meiosis, it will segregate to form 8 separate gametes.
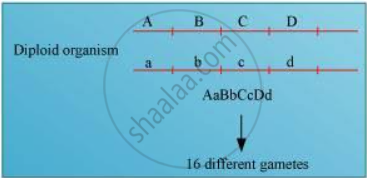
If the genes are not linked, then the diploid organism will produce 16 different gametes. However, if the genes are linked, the gametes will reduce their number as the genes might be linked and the linked genes will be inherited together during the process of meiosis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the following term with example.
Incomplete dominance
Name the pattern of inheritance where F1 phenotype
does not resemble either of the two parents and is in between the two.
Two non-allelic genes produce the new phenotype when present together but fail to do so independently, it is called ______.
A recessive allele is expressed in ______.
The inheritance of flower colour in Antirrhinum (dog flower) is an example of ______.
In Antirrhinum (dog flower), phenotypic ratio in F2 generation for the inheritance of flower colour would be ______.
Phenotypic and genotypic ratio is similar in case of ______.
Genotypic and phenotypic ratio in monohybrid cross remains the same in care of:
If a homozygous red-flowered plant (dominant) crossed with a homozygous white floured plant (recessive) the offspring should be:
In a cross between homozygous recessive and a heterozygous dominant, the phenotypic and genotypic ratios respectively are ______
Which one is an intragenic interaction of genes?
Even if a character shows multiple allelism, an individual will only have two alleles for that character. Why?
In a Mendelian monohybrid cross, the F2 generation shows identical genotypic and phenotypic ratios. What does it tell us about the nature of alleles involved? Justify your answer.
A plant with red flowers was crossed with another plant with yellow flowers. If F1 showed all flowers orange in colour, explain the inheritance.
