Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
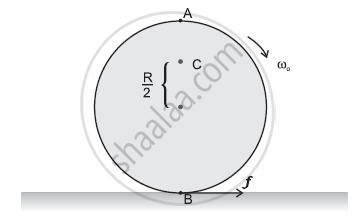
A disc rotating about its axis with angular speed ωois placed lightly (without any translational push) on a perfectly frictionless table. The radius of the disc is R. What are the linear velocities of the points A, B and C on the disc shown in Figure? Will the disc roll in the direction indicated?
उत्तर १
vA = Rωo; vB = Rωo; `v_c = (R/2)omega_o`
The disc will not roll Angular speed of the disc = ωo
Radius of the disc = R
Using the relation for linear velocity, v = ωoR
For point A:
vA = Rωo; in the direction tangential to the right
For point B:
vB = Rωo; in the direction tangential to the left
For point C:
`v_c = (R/2)omega_o` in the direction same as that of vA
The directions of motion of points A, B, and C on the disc are shown in the following figure
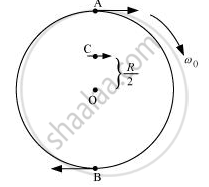
Since the disc is placed on a frictionless table, it will not roll. This is because the presence of friction is essential for the rolling of a body.
उत्तर २
Since `v = romega`
For Point A, `v_A = Romega_0` in the direction of arrow
For point B, `v_B = Romega_0` in the opposite direction of arrow
For point C, `v_C = R/2omega_0` in the direction of arrow
The disc will not roll in the given direction because friction is necessary for the same
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The moon rotates about the earth in such a way that only one hemisphere of the moon faces the earth (see the following figure). Can we ever see the "other face" of the moon from the earth? Can a person on the moon ever see all the faces of the earth?
A sphere rolls on a horizontal surface. If there any point of the sphere which has a vertical velocity?
A body is in pure rotation. The linear speed \[\nu\] of a particle, the distance r of the particle from the axis and the angular velocity \[\omega\] of the body are related as \[\omega = \frac{\nu}{r}.\] Thus
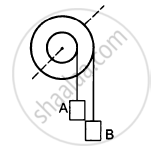
The following figure shows a small wheel fixed coaxially on a bigger one of double the radius. The system rotates about the common axis. The strings supporting A and B do not slip on the wheels. If x and y be the distance travelled by A and B in the same time interval, then _________ .
A sphere is rolled on a rough horizontal surface. If gradually slows down and stops. The force of friction tries to
(a) decrease the linear velocity
(b) increase the angular velocity
(c) increase the linear momentum
(d) decrease the angular velocity.
Find the angular velocity of a body rotating with an acceleration of 2 rev/s2 as it completes the 5th revolution after the start.
A disc of radius 10 cm is rotating about its axis at an angular speed of 20 rad/s. Find the linear speed of a point on the rim.
A disc of radius 10 cm is rotating about its axis at an angular speed of 20 rad/s. Find the linear speed of the middle point of a radius.
A boy is standing on a platform which is free to rotate about its axis. The boy holds an open umbrella in his hands. The axis of the umbrella coincides with that of the platform. The moment of inertia of "the platform plus the boy system" is 3⋅0 × 10−3 kg-m2 and that of the umbrella is 2⋅0 × 10−3 kg-m2. The boy starts spinning the umbrella about the axis at an angular speed of 2⋅0 rev/s with respect to himself. Find the angular velocity imparted to the platform.
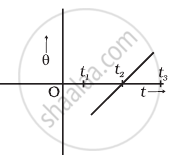
The variation of angular position θ, of a point on a rotating rigid body, with time t is shown in figure. Is the body rotating clock-wise or anti-clockwise?