Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object, irrespective of its position. What kind of lens is this? Draw an outline ray diagram to show the formation of the image. State the position and one more characteristic of the image.
उत्तर
A concave (or diverging) lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object irrespective of its position.
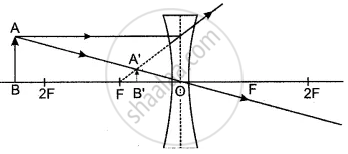
The outline ray diagram showing the formation of the image is given in figure. For the object AB, the image is A’B’.
The image is formed between optical centre O and focus F, in front of the lens.
The image is virtual.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The focal length of a lens is +150 mm. What kind of lens is it and what is its power?
The power of a lens is +2.0D. Its focal length should be :
Express the power (with sign) of a concave lens of focal length 20 cm.
A diverging lens of focal length 20 cm and a converging lens of focal length 30 cm are placed 15 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. Where should an object be placed on the principal axis so that its image is formed at infinity?
Surabhi from std. X uses spectacle. The power of the lenses in her spectacle is 0.5 D.
Answer the following questions from the given information:
- Identify the type of lenses used in her spectacle.
- Identify the defect of vision Surabhi is suffering from.
- Find the focal length of the lenses used in her spectacle.
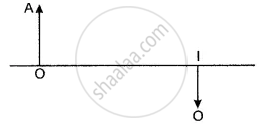
The following diagram shows the object O and the image I formed by a lens. Copy the diagram and on it mark the positions of the lens LL’ and focus (F). Name the lens.
If there is a convex lens of focal length 75 cm and a concave lens of focal length 40 cm, then calculate their combined power and combined focal length.
Focal length : metre : : power of lens : _______
Increase in the converging power of eye lens cause ‘hypermetropia'
The focal length of a concave lens is 20 cm. The focal length of a convex lens is 25 cm. These two are placed in contact with each other. What is the power of the combination? Is it diverging, converging or undeviating in nature?
