Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Rewrite the image distances in the correct order.
उत्तर
Since the focal length is a constant quantity, we have to pair the object distance(u) and the image distance (v) such that the focal length always comes out to be the same. From the above argument, we get the correct order of the image distance as 100 , 60 , 40 , 30 and 24. The reason being, as the object is carried far from a convex lens, the image is formed closer to the lens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from air into an optically denser medium.
Distinguish between a convex lens and concave lens. Which of the two is a converging lens : convex lens of concave lens?
A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. At which of the following position should an object be placed so that this convex lens may act as a magnifying glass?
(a) 15 cm
(b) 7 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 25 cm
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate focal length of the lens.
An object 3 cm high is placed 24 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find by calculations, the position, height and nature of the image.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens. State three characteristics of the image.
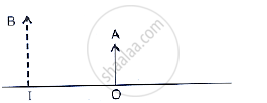
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as an erecting lens in terrestrial telescope.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as in searchlight.
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
