Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A student obtained on a screen the sharp image of a candle flame placed at the farther end of laboratory table using a concave mirror. For getting better value of focal length of the mirror, the teacher suggested to him to focus the sun. What should the student do?
(A) Should move the mirror away from the screen.
(B) Should move the mirror towards the screen.
(C) Should move the mirror and screen both towards the sun.
(D) Should move only the screen towards the sun.
उत्तर
Initially, the screen was placed beyond the focus to capture the image of the candle flame placed at a finite distance from the mirror. So, in order to capture a bright image of the Sun (at infinity) on the screen, the student should move the mirror towards the screen.
Hence, the correct option is B.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | A plane mirror | (i) | Used as a magnifying glass. |
| (b) | A convex mirror | (ii) | Can form image of objects spread over a large area. |
| (c) | A convex lens | (iii) | Used by dentists to see enlarged image of teeth. |
| (d) | A concave mirror | (iv) | The image is always inverted and magnified. |
| (e) | A concave lens | (v) | The image is erect and of the same size as the object. |
| (vi) | The image is erect and smaller in size than the object. |
A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of 30°. What is the angle of reflection
Define (a) centre of curvature (b) radius of curvature (c) pole (d) principal axis, and (e) aperture, of a spherical mirror with the help of a labelled diagram
State the position of object for which the image formed by a concave mirror is of same size.
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Radius of curvature
Define the term Focus of a concave mirror.
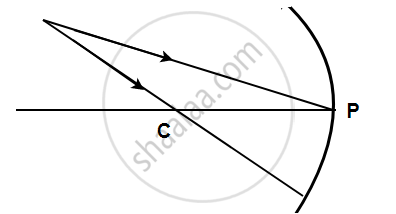
Complete the following diagrams shown in the following figures by drawing the reflected rays.
The spherical mirror with a reflecting surface curved inward is called
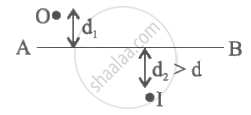
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at the point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be: