Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
"A trait may be inherited, but may not be expressed." Justify this statement with the help of a suitable example.
उत्तर १
Let us take the following example to justify the above statement.
Mendel crossed tall pea plants with dwarf pea plants.
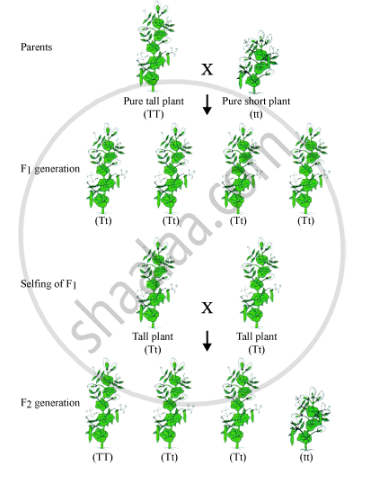
Mendel's Observation
F1 generation contained all tall plants. When F1 generation underwent selfing, the trait that was unexpressed in F1(dwarf) was observed in some F2 progeny. Thus, both traits, tall and dwarf, were expressed in F2 generation in the ratio 3:1.
The above experiment indicates that although both the traits of tallness and shortness were inherited in F1 plants, only the tallness trait was expressed. This shows that traits may not show up in an individual but are passed on to the next generation.
उत्तर २
Some traits are determined by the combined effect of more than one pair of genes. These are referred to as polygenic or continuous, traits.
An example of this is human stature. The combined size of all of the body parts from head to foot determines the height of an individual. There is an additive effect. The sizes of all of these body parts are, in turn, determined by numerous genes. Human skin, hair, and eye color are also polygenic traits because they are influenced by more than one allele at different loci. The result is the perception of continuous gradation in the expression of these traits.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is a gene?
A cross was made between pure breeding pea plants one with round and green seeds and the other with wrinkled and yellow seeds.
(a) Write the phenotype of F1 progeny. Give reason for your answer.
(b) Write the different types of F2 progeny obtained along with their ration when F1 progeny was selfed.
Mendel in one of his experiments with pea plants crossed a variety having round seed with one having wrinkled seeds. Write his observations, giving reasons, of F1 and F2 progeny
To perform an experiment to identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed, first of all you require a dicot seed. Select dicot seeds from the following group:
Wheat, Gram, Maize, Pea, Barley, Ground-nut
(A) Wheat, Gram and Pea
(B) Gram, Pea and Ground-nut
(C) Maize, Pea and Barley
(D) Gram, Maize and Ground-nut
Fill in the following blank with suitable word .
In pea plants, the gene for dwarfness is ..............whereas that for tallness is ............ .
Using height (tallness/dwarfness) of a plant as an example, show that genes control the characteristics or traits in an organism.
The following results were obtained by a scientist who crossed the F1 generation of pure-breeding parents for round and wrinkled seeds.
| Dominant trait | Recessive trait | No. of F2 offspring |
| Round seeds | Wrinkled seeds | 7524 |
From these results, it can be concluded that the actual number of round seeds he obtained was ______
Only one of the following characteristic of the parents can be inherited by their children. This one is :
(a) deep scar on chin
(b) snub nose
(c) technique of swimming
(d) cut nose
Explain Mendel’s law of independent inheritance. Give one example.
What is genetics?
