Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An electric field is applied to a semiconductor. Let the number of charge carries be nand the average drift speed by v. If the temperature is increased,
विकल्प
both n and v will increase
n will increase but v will decrease
v will increase but n will decrease
both n and v will decrease.
उत्तर
n will increase but v will decrease
As we increase the temperature, additional electron‒hole pairs are created in a semiconductor. As a result, the number of charge carriers increases.
Now, drift velocity ( vd) is given by
`vd =(-eEr)/m`
As the temperature increases, the relaxation time of charge carriers (T) decreases. As a result, vd decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw energy band diagrams of an n-type and p-type semiconductor at temperature T > 0 K. Mark the donor and acceptor energy levels with their energies.
Write two characteristic features to distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors ?
In semiconductors, thermal collisions are responsible for taking a valence electron to the conduction band. Why does the number of conduction electrons not go on increasing with time as thermal collisions continuously take place?
When an impurity is doped into an intrinsic semiconductor, the conductivity of the semiconductor
Two identical capacitors A and B are charged to the same potential V and are connected in two circuits at t = 0 as shown in figure. The charges on the capacitors at a time t = CRare, respectively,
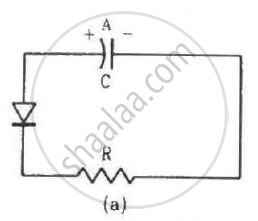
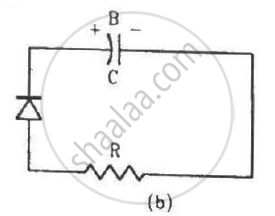
An incomplete sentence about transistors is given below:
The emitter−..... junction is __ and the collector−..... junction is __. The appropriate words for the dotted empty positions are, respectively,
The impurity atoms with which pure silicon may be doped to make it a p-type semiconductor are those of
(a) phosphorus
(b) boron
(c) antimony
(d) aluminium.
Calculate the number of states per cubic metre of sodium in 3s band. The density of sodium is 1013 kgm−3. How many of them are empty?
Indium antimonide has a band gap of 0.23 eV between the valence and the conduction band. Find the temperature at which kT equals the band gap.
The band gap for silicon is 1.1 eV. (a) Find the ratio of the band gap to kT for silicon at room temperature 300 K. (b) At what temperature does this ratio become one tents of the value at 300 K? (Silicon will not retain its structure at these high temperatures.)
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
The product of the hole concentration and the conduction electron concentration turns out to be independent of the amount of any impurity doped. The concentration of conduction electrons in germanium is 6 × 1019 per cubic metref conduction electrons increases to 2 × 1023 per cubic metre. Find the concentration of the holes in the doped germanium.. When some phosphorus impurity is doped into a germanium sample, the concentration o
Two radioactive substances A and B have decay constants 3λ and λ respectively. At t = 0 they have the same number of nuclei. The ratio of the number of nuclei of A to those of B will be `1/"e"` after a time interval:
In a common-base circuit calculate the change in the base current if that in the emitter current is αmA and a = 0.98
In a semiconductor, the forbidden energy gap between the valence, band and the conduction band is of the order of
The valance of an impurity added to germanium crystal in order to convert it into p-type semiconductor is
In a common base configuration Ie = 1 mA α = 0.95 the value of base current is
The reaction between α and β parameter of a transistor is given by
- Assertion (A): In insulators, the forbidden gap is very large.
- Reason (R): The valence electrons in an atom of an insulator are very tightly bound to the nucleus.
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
What is meant by “Forbidden band" of energy levels?
