Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
How does the structure of actin and myosin help in muscle contraction?
उत्तर
- Myosin filament:

- Each myosin filament is a polymerized protein. Many meromyosins (monomeric proteins) constitute one thick filament.
- Myosin molecule consists of two heavy chains (heavy meromyosin / HMM) coiled around each other forming a double helix. One end of each of these chains is projected outwardly is known as a cross bridge. This end folds to form a globular protein mass called myosin head.
- Two light chains are associated with each head forming 4 light chains/light meromyosin / LMM.
- Myosin head has a special ATPase activity. It can split ATP to produce energy.
- Myosin contributes 55% of muscle proteins.
- In sarcomere, myosin tails are arranged to point towards the centre of the sarcomere and the heads point to the sides of the myofilament band.
- Actin filament:
It is a complex type of contractile protein. It is made up of three components: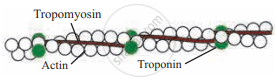
- F actin: It forms the backbone of actin filament. F actin is made up of two helical strands. Each strand is composed of polymerized G actin molecules. One ADP molecule is attached to G actin molecule.
- Tropomyosin: The actin filament contains two additional protein strands that are polymers of tropomyosin molecules. Each strand is loosely attached to an F actin. In the resting stage, tropomyosin physically covers the active myosin-binding site of the actin strand.
- Troponin: It is a complex of three globular proteins, is attached approx. 2/3rd distance along each tropomyosin molecule. It has affinity for actin, tropomyosin and calcium ions. The troponin complex is believed to attach the tropomyosin to the actin. The strong affinity of troponin for calcium ions is believed to initiate the contraction process.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Describe the important steps in muscle contraction.
Answer the following question.
How is the structure of sarcomere suitable for the contractility of the muscle? Explain its function according to sliding filament theory.
Name the filaments present in the sarcomere.
Exchange of calcium between bone and extracellular fluid takes place under the influence of certain hormones. What will happen if very less amount of Ca++ is in the extracellular fluid?
Radha was running on a treadmill at a great speed for 15 minutes continuously. She stopped the treadmill and abruptly came out. For the next few minutes, she was breathing heavily/fast. Answer the following questions.
What happened to her muscles when she did strenuously exercised?
Radha was running on a treadmill at a great speed for 15 minutes continuously. She stopped the treadmill and abruptly came out. For the next few minutes, she was breathing heavily/fast. Answer the following questions.
How did her breathing rate change?
What is the source of energy for muscle contraction?
Calcium ion concentration in blood affects muscle contraction. Does it lead to tetany in certain cases? How will you correlate fluctuation in blood calcium with tetany?
Explain sliding filament theory of muscle contraction with neat sketches.
How does a muscle shorten during its contraction and return to its original form during relaxation?
