Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
How would you demonstrate that yeast can respire both aerobically and anaerobically?
उत्तर
Respiration in yeast can be demonstrated with the help of an experiment.
Anaerobic respiration in yeast:
- A pinch of dry baker’s yeast suspended in water containing 10ml of 10% glucose in a test tube (test tube A).
- The surface of the liquid is covered with oil to prevent the entry of air and the test tube is closed tightly with a rubber stopper to prevent leakage.
- One end of a short-bent glass tube is inserted through it to reach the air inside the tube.
- Other end of the glass tube is connected by a polyethylene or rubber tubing to another bent glass tube fitted into a stopper.
- The open end of the glass tube (delivery tube) is dipped into lime water containing in a test tube (Tube B).
- Stoppers of both the tubes are fitted tightly to prevent leakage of gases. The first test tube is placed in warm water (37° C-38° C) in a beaker.
- Lime water gradually turns milky, indicating the evolution of carbon dioxide from the yeast preparation.
- The level of the lime water in the delivery tube does not rise, showing that there is no decline in the volume of gas in test tube A and consequently no utilization of oxygen by yeast.
- Preparation is stored for a day or two.
- When we open the stopper of tube A we will notice a smell of alcohol indicating the formation of ethanol.
- From this activity it may be inferred that yeast respires anaerobically to ferment glucose to ethanol and carbon dioxide.
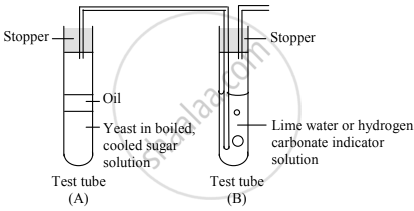
Aerobic respiration in yeast:
The experiment explained in above can be carried out for demonstrating aerobic respiration in yeast.
- If the level of the lime water in the test tube B rises, indicating intake of oxygen, hence the level of volume of gas rises.
- The preparation tube is stored for a day or two, if no smell of alcohol is noticed it indicates that the yeast respires aerobically.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blank.
Bronchi divide into smaller tubes called .....................
Name the cell organelle in which Kreb's take place.
Name the following:
The respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.
Answer the following question.
Write explanatory notes on Glycolysis.
Tabulate the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Which is formed during anaerobic respiration?
____________ ATPs will be effectively produced during the production of 1 molecule of acetyl-CoA from 1 molecule of pyruvic acid.
Match the Column I (ETS Complex) to Column II (Characteristic) and select the correct option.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| i. | Complex I | a. | Succinate dehydrogenase |
| ii. | Complex II | b. | Cytochrome oxidase |
| iii. | Complex III | c. | NADH dehydrogenase |
| iv. | Complex IV | d. | Cytochrom bc1 complex |
Find out the number of ATP molecules produced through oxidative phosphorylation of NADH, produced through breakdown of 12 molecules of pyruvic acid in Kerb cycle?
Glycolysis occurs in ____________.
