Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Why do we need to know the center of mass of an object? For which objects, its position may differ from that of the center of gravity?
उत्तर
- Centre of the mass of an object allows us to apply Newton’s laws of motion to finite objects (objects of measurable size) by considering these objects as point objects.
- For objects in non–uniform gravitational field or whose size is comparable to that of the Earth (size at least few thousand km), the position of the centre of mass will differ than that of the centre of gravity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
On what factor does the position of the center of gravity of a body depend?
State a factor on which the position of the centre of gravity of a body depend? Explain your answer with an example.
What is the position of the centre of gravity of a rectangular lamina?
At which point is the centre of gravity situated in a triangular lamina?
A square cardboard is suspended by passing a pin through a narrow hole at its one corner. Draw a diagram to show its rest position. In the diagram, mark the point of suspension by the letter S and the centre of gravity by the letter G.
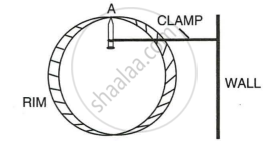
A uniform flat circular rim is balanced on a sharp vertical nail by supporting it at point A, as shown in the figure. Mark the position of the centre of gravity of the rim in the diagram by the letter G.
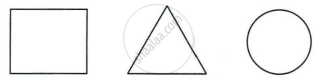
The figure shows three pieces of cardboard of uniform thickness cut into three different shapes. On each diagram draw two lines to indicate the position of the centre of gravity G.
The centre of gravity of a uniform ball is ______.
Following Fig shows piece of cardboard of uniform thickness cut into different shapes. Draw two lines to indicate the position of centre of gravity G.
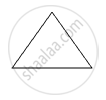
Following Fig shows piece of cardboard of uniform thickness cut into different shapes. Draw two lines to indicate the position of centre of gravity G.
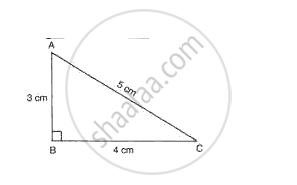
Fig. shows the dimensions of an acute angled triangle. By geometrical construction mark the C.G. of the triangle.
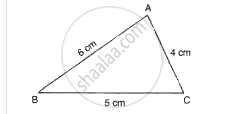
A right-angled triangle cardboard piece is placed as shown in fig. 7. Redraw the diagram showing the relative position of the vertices of the triangle when it is suspended by a pin from the hole A. Explain why the position changes?
Give scientific reason for the following:
There are chances of toppling when a truck takes a sharp turn especially when it is not fully loaded
The centre of gravity of a hollow cone of height h is at distance x from its vertex where the value of x is ______.
Where does the position of centre of gravity lie for a circular lamina
Explain why a tight rope-walker, often holds a long pole in his hands when in action.
Explain why a ship loaded with light goods is more liable to be overturned than the one loaded with heavy goods.
Explain why Standing passengers are not allowed on the upper deck of a double-decker bus.
Explain the term ‘centre of gravity’ of a body.
A boy of mass 40 kg runs up a height of 30 steps, each 20 cm high. Find:
(i) The force of gravity acting on the boy.
(ii) The work done by the boy against gravity. (Take g = 9.8 ms−2)
In ______ equilibrium, the centre of gravity remains at the same height when it is displaced.
What is centre of gravity ?
If mean radius of earth is R, its angular velocity is ro and the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth is g, then the cube of the radius of the orbit of satellite will be ____________.
When this triangular lamina is suspended freely from any one vertex, what is the moment of force produced by its own weight in its rest position?
