Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
At what distance from the mean position is the kinetic energy of a particle performing S.H.M. of amplitude 8 cm, three times its potential energy?
उत्तर
Data: A = 8 cm, KE = 3 PE
KE = `1/2`k(A2 − x2) and PE = `1/2`kx2
Given, KE = 3PE.
∴ `1/2`k(A2 − x2) = `3(1/2"kx"^2)`
∴ A2 − x2 = 3x2
∴ 4x2 = A2
∴ the required displacement is
x = `±"A"/2=±8/2` = `±` 4 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A needle of a sewing machine moves along a path of amplitude 4 cm with a frequency of 5 Hz. Find its acceleration `(1/30)` s after it has crossed the mean position.
Potential energy of a particle performing linear S.H.M. is 0.1 π2x2 joule. If the mass of the particle is 20 g, find the frequency of S.H.M.
Two S.H.M.’s have zero phase difference and equal amplitudes A. The resultant amplitude on their composition will be ______
A simple pendulum moves from one end to the other in ¼ second. What is its frequency?
What is the amplitude of S.H.M.
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is 1.7 m/s2. What is the time period of a simple pendulum on the surface of the moon if its time period on the surface of the earth is 3.5 s? (g on the surface of earth = 9.8 m/s2)
A particle performing S.H.M. has velocities of 8 cm/s and 6 cm/s at displacements of 3 cm and 4 cm respectively. Calculate the amplitude and period of S.H.M.
The total energy of the body executing S.H.M. is E. The kinetic energy of the body, when the displacement is half of the amplitude is ______.
When a mass is hung from a light spring, the spring extends by 10 cm. If the mass is pulled down and let go, it executes S.H.M. with a time period (g = 10 m/s2) ____________.
A particle is executing S.H.M. with amplitude of 4 cm and time period 12 s. The time taken by the particle in going from its mean position to a position of displacement equal to 2 cm is T1 The time taken from this displaced position of 2 cm to reach the extreme position is T2. T1/ T2 will be____________.
If 'x', 'v' and 'a' denote the displacement, velocity and acceleration of a particle respectively executing SHM of periodic time t, then which one of the following does not change with time?
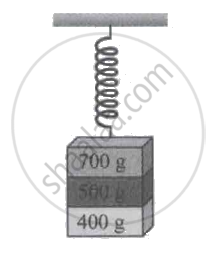
Three masses 700 g, 500 g, and 400 g are suspended at the end of a spring and are in equilibrium as shown in figure. When the 700 g mass is removed, the system oscillates with a period of 3 seconds; when the 500 g mass is also removed, it will oscillate with a period of ____________.
The amplitude of sound is doubled and the frequency is reduced to one fourth. The intensity of sound at the same point will be ____________.
A horizontal spring executes S.H.M. with amplitude 'A1', when mass 'm1' is attached to it, When it passes through mean position another mass 'm2' is placed on it. Both masses move together with amplitude 'A2'. Therefore A2 : A1 is ______
A mass M attached to a horizontal spring executes S.H.M. of amplitude A1. When the mass M passes through its mean position, then a smaller mass m is placed over it and both of them move together with amplitude A2. The ratio of `(A_1/A_2)` is ______
Two trains are moving towards each other with speeds of 20m/s and 15 m/s relative to the ground. The first train sounds a whistle of frequency 600 Hz. The frequency of the whistle heard by a passenger in the second train before the train meets, is ______. (the speed of sound in air is 340 m/s)
A mass is suspended from a vertical spring which is executing S.H.M. of frequency 5 Hz. The spring is unstretched at the highest point of oscillation. Maximum speed of the mass is ______. [acceleration due to gravity g = 10 m/s2]
A mass m1 connected to a horizontal spring performs SHM with amplitude A. While mass m1 is passing through mean position, another mass m2 is placed on it so that both the masses move together with amplitude A1. The ratio of `"A"_1/"A"` is ______. (m2 < m1)
The motion of a particle varies with time according to the relation y = a sin ω t + a cos ω t. Then, ______.
Light of a certain colour has 2500 waves to the millimetre in air. What is its frequency?
