Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Based on VB theory explain why \[\ce{[Cr(NH3)6]^3+}\] is paramagnetic, while \[\ce{[Ni(CN)4]^2-}\] is diamagnetic.
उत्तर
1. \[\ce{[Cr(NH3)6]^3+}\]
In this complex, Cr is in the +3 oxidation state. Electronic configuration of Cr atom. Electronic configuration of Cr3+ ion
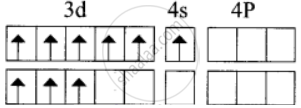
Hybridisation and formation of [Cr(NH3)6]3+ Complex
Due to the presence of three unpaired electrons in [Cr(NH3)6]3+ it behaves as a paramagnetic substance.
The spin magnetic moment,
µs = `"g" sqrt(3(3 + 2)) = "g" sqrt(15)` = 3.87 BM
[Cr(NH3)6]3+ is an inner orbital octahedral complex.
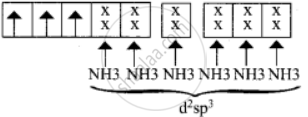
2. \[\ce{[Ni(CN)4]^2-}\]
In this complex, Ni is in the +2 oxidation state. Electronic configuration of Ni atom. Electronic configuration of Ni2+ ion. Hybridisation and formation of \[\ce{[Ni(CN)4]^2-}\] Complex

Since CN– is a strong field ligand, hence the electrons in 3d orbitals are forced to pair up and there is no unpaired electron in [Ni(CN)4]2, hence it should be a diamagnetic substance.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Oxidation state of Iron and the charge on the ligand NO in [Fe(H2O)5NO]SO4 are ____________.
In which of the following coordination entities the magnitude of Δ0 will be maximum?
Give an example of coordination compound used in medicine and two examples of biologically important coordination compounds.
[Ti(H2O)6]3+ is coloured, while [Sc(H2O)6]3+ is colourless – explain.
Classify the following ligand based on the number of donor atoms.
NH3
Classify the following ligand based on the number of donor atoms.
en
Classify the following ligand based on the number of donor atoms.
ox2−
Classify the following ligand based on the number of donor atoms.
pyridine
What is the coordination entity formed when excess of liquid ammonia is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate?
On the basis of VB theory explain the nature of bonding in \[\ce{[Co(C2O4)3]^3-}\].
