Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Briefly describe the Given structure - Eye
उत्तर
Eye: Eyes are spherical structures that consist of three layers.
(a) The outer layer is composed of sclera and cornea.
(i) Sclera is an opaque tissue that is usually known as white of the eye. It is composed of a dense connective tissue.
(ii) Cornea is a transparent anterior portion of eye that lacks blood vessels and is nourished by lymph from the nearby area. It is slightly bulged forward and helps in focusing light rays with the help of lens.
(b) The middle layer of eye is vascular in nature and contains choroid, ciliary body, and iris.
(i) Choroid lies next to the sclera and contains numerous blood vessels that provide nutrients and oxygen to the retina and other tissues.
(ii) Ciliary body: The choroid layer is thin over posterior region and gets thickened in the anterior portion to form ciliary body. It contains blood vessels, ciliary muscles, and ciliary processes.
(iii) Iris: At the junction of sclera and cornea, the ciliary body continues forward to form thin coloured partition called iris. It is the visible coloured portion of eye.
The eye contains a transparent, biconvex, and elastic structure just behind the iris. It is known as lens. The lens is held in position by suspensory ligaments attached to the ciliary body. The lens divides the eye ball into two chambers – an anterior aqueous and posterior vitreous chamber.
(c) The innermost nervous coat of eye contains retina. Retina is the innermost layer. It contains three layers of cells – inner ganglion cells, middle bipolar cells, and outermost photoreceptor cells. The receptor cells present in the retina are of two types – rod cells and cone cells.
(a) Rod cells –The rods contain the rhodopsin pigment (visual purple) that is highly sensitive to dim light. It is responsible for twilight vision.
(b) Cone cells –The cones contain the iodopsin pigment (visual violet) and are highly sensitive to high intensity light. They are responsible for daylight and colour visions.
The innermost ganglionic cells give rise to optic nerve fibre that forms optic nerve in each eye and is connected with the brain
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Briefly describe the Given structure - Ear
Compare the following:
Central neural system (CNS) and Peripheral neural system (PNS)
Explain the following process:
Polarisation of the membrane of a nerve fibre
Explain the following process:
Depolarisation of the membrane of a nerve fibre.
Explain the following processes:
Conduction of a nerve impulse along a nerve fibre
Distinguish between Afferent neurons and efferent neurons.
Examine the diagram of the two cell types A and B given below and select the correct option.
The respiratory centre is present in the ______.
The abundant intracellular cation is ______.
Several statements are given here in reference to cone cells which of the following option indicates all correct statements for cone cells?
Statements
- Cone cells are less sensitive in bright light than Rod cells
- They are responsible for colour vision
- Erythropsin is a photo pigment which is sensitive to red colour light
- They are present in fovea of retina
Which of the following statement concerning the somatic division of the peripheral neural system is incorrect?
The choroid plexus secretes cerebrospinal fluid. List the function of it.
The function of our visceral organs is controlled by ______.
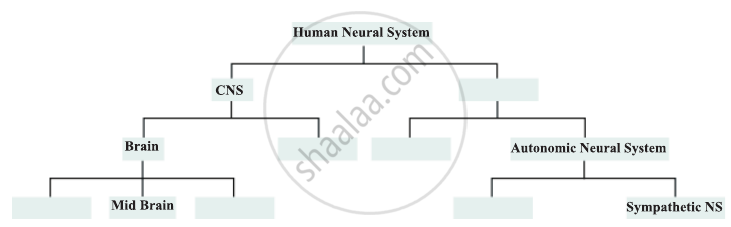
The major parts of the human neural system is depicted below. Fill in the empty boxes with appropriate words.
Neural system and computers share certain common features. Comment in five lines. (Hint: CPU, input-output devices).
