Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Briefly explain ‘centrifugal force’ with suitable examples.
उत्तर
To use Newton’s first and second laws in the rotational frame of reference, we need to include a Pseudo force called centrifugal force. This centrifugal force appears to act on the object with respect to rotating frames.
Circular motion can be analyzed from two different frames of reference. One is the inertial frame (which is either at rest or in uniform motion) where Newton’s laws are obeyed. The other is the rotating frame of reference which is a non – inertial frame of reference as it is accelerating.
When we examine the circular motion from these frames of reference the situations are entirely different. To use Newton’s first and second laws in the rotational frame of reference, we need to include a pseudo force called ‘centrifugal force’. This ‘centrifugal force’ appears to act on the object with respect to rotating frames. To understand the concept of centrifugal force, we can take a specific case and discuss it as done below.

Free body diagram of a particle including the centrifugal force
Free body diagram of a particle including the centrifugal force Considers the case of a whirling motion of a stone tied to a string. Assume that the stone has angular velocity ω in the inertial frame (at rest). If the motion of the stone is observed from a frame that is also rotating along with the stone with the same angular velocity ω then, the stone appears to be at rest.
This implies that in addition to the inward centripetal force – mω2r there must be an equal and opposite force that acts on the stone outward with value +mω2r . So the total force acting on the stone in a rotating frame is equal to zero (-mω2r + mω2 r = 0). This outward force +mω2r is called the centrifugal force. The word ‘centrifugal’ means ‘flee from the center’.
Note that the ‘centrifugal force’ appears to act on the particle, only when we analyze the motion from a rotating frame. With respect to an inertial frame, there is only a centripetal force which is given by the tension in the string. For this reason, centrifugal force is called a ‘pseudo force’. A pseudo force has no origin. It arises due to the noninertial nature of the frame considered. When circular motion problems are solved from a rotating frame of reference, while drawing a free body diagram of a particle, the centrifugal force should necessarily be included as shown in the figure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The centrifugal force appears to exist ______
Choose the correct statement from the following.
If a person moving from pole to equator, the centrifugal force acting on him ______
What is the meaning of ‘pseudo force’?
A car takes a turn with a velocity of 50 ms-1 on the circular road of a radius of curvature of 10 m. calculate the centrifugal force experienced by a person of mass 60 kg inside the car?
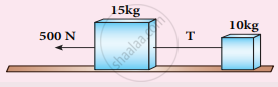
Two bodies of masses 15 kg and 10 kg are connected with light string kept on a smooth surface. A horizontal force F=500 N is applied to a 15 kg as shown in the figure. Calculate the tension acting in the string?
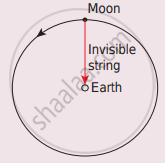
Imagine that the gravitational force between Earth and Moon is provided by an invisible string that exists between the Moon and Earth. What is the tension that exists in this invisible string due to Earth’s centripetal force? (Mass of the Moon = 7.34 × 1022 kg, Distance between Moon and Earth = 3.84 × 108 m)
A bob attached to the string oscillates back and forth. Resolve the forces acting on the bob into components. What is the acceleration experienced by the bob at an angle θ?
Explain the need for banking of tracks.
Explain the similarities and differences of centripetal and centrifugal forces.
