Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Complete the diagram/chart with correct labels/ information. Write the conceptual details regarding it.
उत्तर
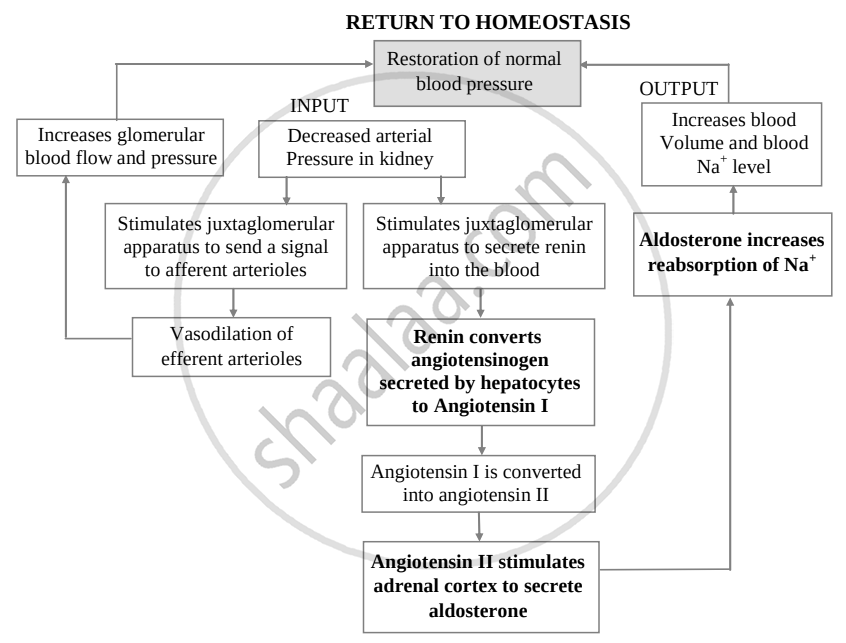
The composition of urine depends upon food and fluid consumed by an individual. There are two ways in which it the composition is regulated. They are as follows:
- Regulating water reabsorption through ADH
- Electrolyte reabsorption through RAAS
- Atrial Natriuretic Peptide
i. Regulating water reabsorption through ADH:
Hypothalamus in the midbrain has special receptors called osmoreceptors which can detect change in osmolarity (measure of total number of dissolved particles per liter of solution) of blood. If osmolarity of blood increases due to water loss from the body (after eating namkeen or due to sweating), osmoreceptors trigger release of Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary). ADH stimulates reabsorption of water from the last part of DCT and the entire collecting duct by increasing the permeability of cells. This leads to a reduction in urine volume and a decrease in osmolarity of blood. Once the osmolarity of blood comes to normal, activity of osmoreceptor cells decreases leading to a decrease in ADH secretion. This is called negative feedback. In case of hemorrhage or severe dehydration too, osmoreceptors stimulate ADH secretion. ADH is important in regulating water balance through the kidneys. In absence of ADH, diuresis (dilution of urine) takes place and a person tends to excrete large amounts of dilute urine. This condition called diabetes insipidus.
ii. Electrolyte reabsorption through RAAS:
Another regulatory mechanism is RAAS (Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System) by Juxta Glomerular Apparatus (JGA). Whenever blood supply (due to change in blood pressure or blood volume) to afferent arteriole decreases (e.g. low BP/dehydration), JGA cells release Renin. Renin converts angiotensinogen secreted by hepatocytes in the liver to Angiotensin I. ‘Angiotensin-converting enzyme’ further modifies Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II, the active form of the hormone. It stimulates the adrenal cortex to release another hormone called aldosterone that stimulates DCT and collecting ducts to reabsorb more Na+ and water, thereby increasing blood volume and pressure.
iii. Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP):
A large increase in blood volume and pressure stimulates the atrial wall to produce atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP). ANP inhibits Na+ and Cl– reabsorption from collecting ducts inhibits the release of renin, reduces aldosterone and ADH release too. This leads to a condition called Natriuresis (increased excretion of Na+ in urine) and diuresis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write True (T) or False (F) for the following statement. Rewrite the false statement in the correct form.
Removal of solid undigested food is excretion
Correct the sequence of the following steps to explain the process of urine formation.
1. Blood enters the glomerulus under high pressure.
2. The filtrate passes through the thin walls of the Bowman’s capsule into the renal tubule
3. As the filtrate, passes through the tubule, water, and many useful substances are reabsorbed by the walls of the blood capillaries.
4. Water and small solutes are filtered in the Bowman’s capsule.
5. The remaining liquid, along with waste is called urine and is collected in the urinary bladder.
6. Blood containing waste material enters the kidneys through the renal artery.
Identify the following structures and explain their significance in renal physiology?
- Juxtaglomerular apparatus
- Podocytes
- Sphincters in the bladder
Stones formed when the urinary tract is infected by urea splitting bacteria are ______
One of the factors which may help to differentiate chronic kidney disease from acute kidney injury is ______
Dialysis is an imperfect treatment because ______
The condition of accumulation of urea in the blood is termed as ______.
What is the procedure advised for the correction of extreme renal failure? Give a brief account of it.
The accumulation of urea in the blood due to malfunctioning of kidneys is referred to as ______.
Which statement is correct regarding the haemodialysis procedure?
