Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Complete the paragraph by choosing the right options given below.
(minimum, near point, 25 cm, farthest, farthest distance, far point)
The _______ distance of an object from a normal eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye, is called the minimum distance of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the _______ of the eye, for a normal human eye, the near point is at _______. The _______ distance of an object from a human eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye is called _______ of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the _______ of the eye.
उत्तर
The minimum distance of an object from a normal eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye, is called the minimum distance of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the near point of the eye, for a normal human eye, the near point is at 25 cm. The farthest distance of an object from a human eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye is called farthest distance of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the far point of the eye.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the term.
Power of accommodation of the eye.
Describe the anatomy of the human eye.
Explain the mechanism of vision.
A person got his eyes tested by an optician. The prescription for the spectacle lenses to be made reads :
Left eye : +2.50 D
Right eye : +2.00 D
Which lens bends the light rays more strongly?
What is the:
far point of a normal human eye?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
To bring light from a near object to a focus on the retina of the eye, the convex eye-lens need to be made....................
The eyes of a person are focused (i) on a nearby object, and (ii) on a distant object, turn by turn. In which case:
the converging power of eye-lens will be the maximum?
What change is made in the eye to enable it to focus on objects situated at different distances? Illustrate your answer with the help of diagrams.
Describe and explain, how a normal eye can see objects lying at various distances clearly.
What are rods and cones in the retina of an eye? Why is our night vision relatively poor compared to the night vision of an owl?
How does the convex eye-lens differ from the ordinary convex lens made of glass?
What happens to the size of pupil of our eye (i) in dim light (ii) in bright light?
If you walk from a dark room into sunlight and back again into dark room, how would your pupils alter in size? What makes this happen?
The size of the pupil of the eye is adjusted by:
(a) cornea
(b) ciliary muscles
(c) optic nerve
(d) iris
An object is moved closer to an eye. What changes must take place in the eye in order to keep the image in sharp focus?
After testing the eyes of a child, the optician has prescribed the following lenses for his spectacles:
Left eye : + 2.00 D
Right eye : + 2.25 D
The child is suffering from the defect of vision called:
(a) short-sightedness
(b) long-sightedness
(c) cataract
(d) presbyopia
The animals of prey have:
(a) two eyes at the front
(b) two eyes at the back
(c) two eyes on the sides
(d) one eye at the front and one on the side
Mention if the following statement is true (T) or false (F) Give reason.
Sometimes medicines dropped into the eyes come into the nose and even throat
Mention if the following statement is true (T) or false (F) Give reason.
Short-sightedness and hyperopia are one and the same thing
Choose the correct answer.
In the chemistry of vision, the photosensitive substance is _________________
Choose the correct answer.
Rods are receptor of ______________
What are the functions of tears?
What is a stereoscopic vision?
Name the following:
The pigmented circular area seen in the eye.
State the Function:
Aqueous humour
Choose the Odd One Out:
For the normal human eye, the near point is at ___________ cm.
Vision defect that increases distance between the lens of the eye and retina of the eye is termed as myopia.
Write an Explanation.
Farthest distance of distinct vision
Write the function of the human eye and label parts of the figure given below.

A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using a lens of power
A student sitting on the last bench can read the letters written on the blackboard but is not able to read the letters written in his text book. Which of the following statements is correct?
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in Figure . In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
 |
 |
 |
 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
Which part of the eye gets affected if someone is suffering from cataract? How is it treated?
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| 1 |
Retina |
a | Pathway of light |
| 2 | Pupil | b |
Far point comes closer |
| 3 | Ciliary muscles | c |
near point moves away |
| 4 | Myopia | d | Screen of the eye |
| 5 | Hypermetropia | f | Power of accommodation |
| Column I | Column II | ||
| 1 | Retina | a | Path way of light |
| 2 | Pupil | b | Far point comes closer |
| 3 | Ciliary muscles | c | near point moves away |
| 4 | Myopia | d | Screen of the eye |
| 5 | Hypermetropia | e | Power of accomodation |
Given below is a cross section of the human eye. Match the structures marked (a) to (e) with their correct functions:
Example: (f) - 6. Holds the lens in position
| Cross section of Human Eye | Functions | |
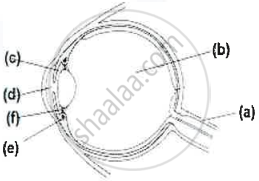 |
1. | Protects retina |
| 2. | Regulates the size of the pupil | |
| 3. | Alters the shape of the lens | |
| 4. | Keeps the lens moist | |
| 5. | Transmits nerve impulses to brain | |
| 6. | Holds the lens in position |
Where is the following located?
Yellow spot
