Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Assume that the temperature of the water at the bottom of the lake remains constant at 4°C as the ice forms on the surface (the heat required to maintain the temperature of the bottom layer may come from the bed of the lake). The depth of the lake is 1.0 m. Show that the thickness of the ice formed attains a steady state maximum value. Find this value. The thermal conductivity of water = 0.50 W m−1°C−1. Take other relevant data from the previous problem.
उत्तर
Let the point upto which ice is formed is at a distance of x m from the top of the lake.
Under steady state, the rate of flow of heat from ice to this point should be equal to the rate flow of heat from water to this point.
Temperature of the top layer of ice = −10°C
Temperature of water at the bottom of the lake = 4°C
Temperature at the point upto which ice is formed = `((DeltaQ)/(Deltat))_{ice} = ((DeltaQ)/(Deltat))_{water}`
`k_{ice}/(x/(Axx10)`= `K_{water}/((1-x)/(Axx4)`
`(1.7 xx 10)/x = (0.5xx4)/(1-x)`
`(1.7)/x = (0.5xx4)/(1-x)`
17 - 17x = 2x
`⇒ x =17/19 = 0.89 m`
`⇒ x = 89 cm`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give reason of Ice floats on water.
How does the anomalous expansion of water help aquatic organisms in cold climates?
Explain the following:
How can you relate the formation of water droplets on the outer surface of a bottle taken out of refrigerator with formation of dew?
Draw a graph to show the variation in density of water with temperature in the range from 0°C to 10°C.
Explain the following
Fishes survive in ponds even when the atmospheric temperature is well below 0°C.
Explain the following
A hollow glass sphere which floats with its entire volume submerged in water at 4°C, sinks when water is heated above 4°C.
Draw a graph between volume and temperature, when 5 cm3 of ice at -10°C is heated to form water at +10°C.
A deep pond of water has its top layer frozen. What will be the likely temperature of water layer just in contact with ice?
In cold countries, the water pipes are covered with poor conductors. Why?
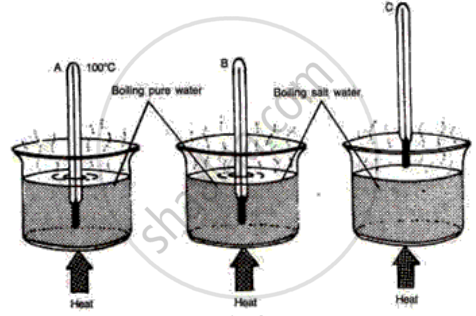
The following diagrams illustrate three situations involving thermometers which are labeled A, Band C. In each situation the thermometers indicate different readings.
(i) What do you expect the approximate reading of the thermometer B and C would be? Give a reason for your answer.
(ii) How would the readings of A and B help you in calibrating a thermometer?
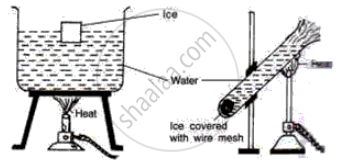
Study the following diagrams and write down your observations.
Give reasons for the following:
Even when the water in the lakes is frozen, fish can survive.
When the temperature of water decreases below 4 °C it’s volume _______.
_______ apparatus is used to study the anomalous behaviour of water.
