Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider three converging lenses L1, L2 and L3 having identical geometrical construction. The index of refraction of L1 and L2 are \[\mu_1 \text{ and } \mu_2\] respectively. The upper half of the lens L3 has a refractive index \[\mu_1\] and the lower half has \[\mu_2\] following figure . A point object O is imaged at O1 by the lens L1 and at O2 by the lens L2placed in same position. If L3 is placed at the same place,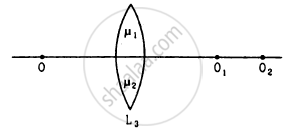
(a) there will be an image at O1
(b) there will be an image at O2.
(c) the only image will form somewhere between O1 and O2
(d) the only image will form away from O2.
उत्तर
(a) there will be an image at O1
(b) there will be an image at O2
The lens L1 converges the light at point O1 and lens L2 converges the light at O2. As the upper half of lens L3 has a refractive index equal to that of L1, it will converge the light at O1 and thus the image will be formed at O1. Also, the lower half of lens L3 has a refractive index equal to that of lens L2, it will converge the light at O2 and thus the image will be formed at O2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the power of a lens.
What does sign of power (+ve or –ve) indicate?
State power of a lens S.I. unit.
What is the focal length of a convex lens of focal length 30 cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm? Is the system a converging or a diverging lens? Ignore thickness of the lenses.
(a) At what distance should the lens be held from the figure in order to view the squares distinctly with the maximum possible magnifying power?
(b) What is the magnification in this case?
(c) Is the magnification equal to the magnifying power in this case? Explain.

Ranbir claims to have obtained an image twice the size of the object with a concave lens. Is he correct? Give a reason for your answer.
What can you see in a completely dark room? If you switch on an electric bulb in this dark room as a light source, explain how you could now see:
(a) the electric bulb
(b) a piece of white paper
What is the nature of a lens whose power is, −4 D?
A converging lens has a focal length of 50 cm. The power of this lens is:
State the condition for the following a lens has both its focal lengths equal .
State the condition for the following a ray passes undeviated through the lens .
A double convex lens has focal length 25 cm. The radius of curvature of one of the surfaces is double of the other. Find the radii, if the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5.
What is meant by the power of accommodation produced?
Which lens has more power a thick lens or a thin lens?
The power of a lens is +2.0 D. Find its focal length and state the kind of lens.
A convex lens is of focal length 20 cm. Find its power.
The power of lens depends on the focal length of the lens

The above lens has a focal length of 10 cm. The object of height 2 mm is placed at a distance of 5 cm from the pole. Find the height of the image.
Define power of a lens. What is its unit? One student uses a lens of focal length 50 cm and another of –50 cm. What is the nature of the lens and its power used by each of them?
