Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define ampere and volt with respect to Ohm’s law.
उत्तर
Ampere: It is the S.I. unit of current. If a current flows in a conductor of resistance of 1Ω, when the potential difference across its ends is 1 volt, the current is said to be 1 ampere, i.e.,
1 ampere = 1 volt/1 ohm
Volt: It is the S. I. unit of potential difference. If a current of 1 ampere flows in a conductor of resistance 1 ohm, then potential difference across its ends is said to be 1 volt, i.e.,
1 volt = 1 ampere × 1 ohm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
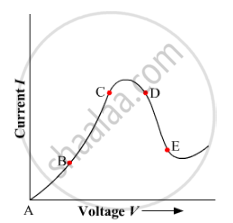
Graph showing the variation of current versus voltage for a material Ga As is shown in the figure. Identify the region of
(i) negative resistance
(ii) where Ohm's law is obeyed.
Name the physical quantity whose unit is "ohm".
A resistance of 40 ohms and one of 60 ohms are arranged in series across 220 volt supply. Find the heat in joules produced by this combination of resistances in half a minute.
State Ohm’s law and draw a neat labelled circuit diagram containing a battery, a key, a voltmeter, an ammeter, a rheostat and an unknown resistance to verify it.
Which of the following is an ohmic resistance?
A wire of resistance 3 ohm and length 10 cm is stretched to length 30 cm. Assuming that it has a uniform cross section, what will be its new resistance?
Show by a diagram how two resistors R1 and R2 are joined in parallel. Obtain an expression for the total resistance of the combination.
An ammeter placed in series with an electric radiator reads 0.5 amps and a voltmeter placed across it reads 230 volts. What is the resistance of the radiator?
A metal rod of length 10 cm and a rectangular cross-section of 1 cm × `1/2` cm is connected to a battery across opposite faces. The resistance will be ______.
Two cells of same emf E but internal resistance r1 and r2 are connected in series to an external resistor R (Figure). What should be the value of R so that the potential difference across the terminals of the first cell becomes zero.