Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define and explain the SN1 mechanism with a suitable example.
उत्तर
This is a substitution nucleophilic unimolecular reaction, meaning that the concentration of just one reactant determines the rate of reaction.
e .g. Alkaline hydrolysis of t-butyl bromide.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3\phantom{......................}CH3}\phantom{......}\\
\phantom{....}|\phantom{..........................}|\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - Br + OH^Θ ->CH3 - C - OH + Br^Θ}\\
\phantom{..}|\phantom{..........................}|\phantom{........}\\
\phantom{}\ce{\underset{(t-Butyl bromide)}{CH3}\phantom{..............}\underset{(t - Butyl alcohol)}{CH3}}\phantom{....}
\end{array}\]
Rate = k[(CH3)3CBr]
It is a two-step reaction.
Step 1: The first step is slow. It involves hetero lysis of the C-X bond in the substrate.
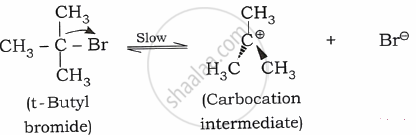
Step 2: The second step is fast. It involves a nucleophilic attack on carbocation and forms a new bond.
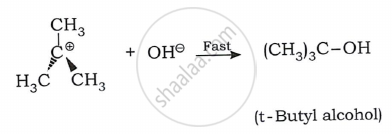
A nucleophile can strike from any direction. As a result, the final product forms a racemic mixture.
