Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define cost. State the behaviour of (a) Total Fixed Cost and (b) Total Variable Cost as output is increased.
उत्तर
Cost is the total expenditure incurred in producing a commodity. In economics, it is the total of actual expenditure incurred on inputs (i.e. explicit cost) and the imputed valued of inputs supplied by owners (i.e. implicit cost).
(a) Total Fixed Cost (TFC):- Total of expenditure incurred by the producer on the purchase or hiring of fixed factors of production. It does not change with change in quantity of output and remains the same whether the output is zero or maximum. For example, the cost of plant and machinery and the wages of permanent staff.
| Output (units) | TFC (in Rupees) |
| 0 | 4 |
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 4 |
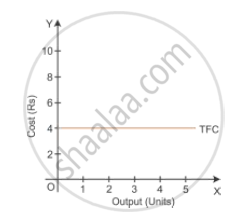
Analysing the TFC schedule and the figure, we can say that TFC remains constant irrespective of the output levels. Therefore, in the short run, TFC is a horizontal curve parallel to the x-axis.
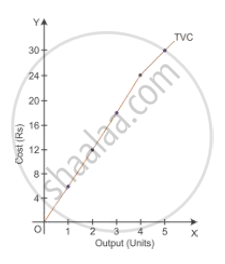
(b) Total Variable Cost (TVC):- Variable cost is the expenditure incurred by the producer on the use of variable factors of production. Variable cost changes with change in quantity of output. For example, the cost of raw materials and fuel expenses.
| Output (units) | TVC (in Rupees) |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 6 |
| 2 | 12 |
| 3 | 18 |
| 4 | 24 |
| 5 | 30 |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An individual is both the owner and the manager of a shop taken on rent. Identify implicit cost and explicit cost from this information. Explain
A producer borrows money to run a business but manages the business himself. Identify implicit cost.
A farmer invests his own saving in doing farmings but hires labour to do work. Identify implicit cost.
A producer starts the business in the building owned by him and borrows money for running it. Identify implicit cost.
When the total fixed cost of producing 100 units is Rs 30and the average variable cost Rs 3, total cost is : (Choose the correct alternative)
(a) Rs 3
(b) Rs 30
(c) Rs 270
(d) Rs 330
Complete the following table:
|
Output (Units) |
Average Fixed Cost (Rs ) |
Marginal Cost (Rs) |
Average Variable Cost (Rs) |
Average Cost (Rs) |
| 1 | 60 | 20 | ... | ... |
| 2 | ... | ... | 19 | ... |
| 3 | 20 | ... | 18 | ... |
| 4 | ... | 18 | ... | ... |
| 5 | 12 | ... | ... | 31 |
From the following total cost and total revenue schedule of a firm, find out the level of output, using marginal cost and marginal revenue approach, at which the firm would be is equilibrium. Give reasons for your answer.
| Output (Units) |
Total Revenue (Rs ) |
Total Cost (Rs ) |
| 1 | 10 | 8 |
| 2 | 18 | 15 |
| 3 | 24 | 21 |
| 4 | 28 | 25 |
| 5 | 30 | 33 |
Complete the following table:
| Output (Units) |
Average Fixed Cost (Rs ) |
Marginal Cost (Rs ) |
Average Variable Cost (Rs ) |
Average Cost (Rs ) |
| 0 | 30 | |||
| 1 | ... | ... | 30 | |
| 2 | 78 | ... | ... | ... |
| 3 | ... | 23 | ... | 10 |
| 4 | ... | ... | 23 | ... |
| 5 | 150 | ... | ... | 6 |
From the following table find out the level of output at which the producer will be in equilibrium (use marginal cost and marginal revenue approach).Give reasons for your answer.
| Output (Units) |
Total Revenue (Rs ) |
Total Cost (Rs ) |
| 1 | 16 | 14 |
| 2 | 30 | 27 |
| 3 | 42 | 39 |
| 4 | 52 | 49 |
| 5 | 60 | 61 |
Complete the following table:
| Output (units) |
Average Fixed Cost (Rs) |
Average Variable Cost (Rs) |
Marginal Cost (Rs) |
Total Cost (Rs) |
| 1 | 120 | 40 | ... | ... |
| 2 | 60 | 56 | ... | 232 |
| 3 | ... | 54 | ... | ... |
| 4 | 30 | ... | 54 | ... |
| 5 | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Distinguish between fixed and variable costs. Give one example of each.
What is meant by cost in economics?
Briefly explain the concept of the cost function.
Answer the following question.
Mention any two examples of the implicit costs incurred by a firm.
