Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the following:
Excretion
उत्तर १
During different metabolic activities taking place in our body, the body produces many substances, of which some are useful and some are useless.
The process of removing useless and harmful metabolic waste substances is called excretion.
उत्तर २
The process of removal of chemical wastes (Mainly Nitrogenous) from the body is known as ''excretion''. It plays an important role in maintaining the homeostatic (steady-state) condition of the body.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following term:
urea
The diagram given below represents an organ system in the human body. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :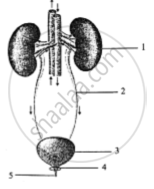
What is the fluid that accumulates in part 3?
Which is the main nitrogenous waste present in it?
Choose the correct answer:
Physiologically urea is produced by the action of an enzyme ______________
Choose the odd one out in the following series:
Kidney, ureter, heart
What are the functions of ureter and urethra?
Name the Following
The gas excreted by the lungs.
Give Technical Term:
Name the organ in which urine is stored before its elimination from the body.
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Ammonia is converted into urea in kidney.
Multiple Choice Question: Profuse sweating take place during heavy muscular exercise. The reason is:
Differentiate the following.
Excretion and Secretion
The human kidneys are located on either side of the vertebral column at the level of ______.
Choose the correct path of urine in our body
Organs that are concerned with the formation, storage, and elimination of urine constitute the ______.
What is the contribution of Joseph E. Murray to Nephrology?
We can produce a concentrated/ dilute urine. This is facilitated by a special mechanism. Identify the mechanism.
The following abbreviations are used in the context of excretory functions, what do they stand for?
DCT
The maximum amount of electrolytes and water (70-80%) from the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in which part of the nephron.
Sodium chloride contained in glomerular filtrate is fully reabsorbed in the renal tubule.
