Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive Mayer’s relation.
उत्तर
- Consider one mole of an ideal gas that is enclosed in a cylinder by a light, frictionless airtight piston.
- Let P, V, and T be the pressure, volume, and temperature respectively of the gas.
- If the gas is heated so that its temperature rises by dT, but the volume remains constant, then the amount of heat supplied to the gas (dQ1) is used to increase the internal energy of the gas (dE). Since the volume of the gas is constant, no work is done in moving the piston.
∴ dQ1 = dE = CV dT ..............(1)
where CV is the molar specific heat of the gas at constant volume. - On the other hand, if the gas is heated to the same temperature, at constant pressure, the volume of the gas increases by an amount say dV. The amount of heat supplied to the gas is used to increase the internal energy of the gas as well as to move the piston backward to allow expansion of gas. The work is done to move the piston dW = PdV.
∴ dQ2 = dE + dW = Cp dT ..............(2)
Where CP is the molar specific heat of the gas at constant pressure. - From equations (1) and (2),
∴ Cp dT = CV dT + dW
∴ (Cp - Cv)dT = PdV ..............(3) - For one mole of gas,
PV = RT
∴ P dV = R dT, since pressure is constant.
Substituting equation (3), we get
(Cp - Cv) dT = R dT
∴ Cp - Cv = R
This is known as Mayer’s relation between CP and CV. - Also, CP = M0SP and CV = M0SV, where M0 is the molar mass of the gas and SP and SV are respective principal specific heats. Thus, M0SP - M0SV = R/J
Where J is the mechanical equivalent of heat.
SP - Sv = `"R"/("M"_0"J")`
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate the mass of ice needed to cool 150 g of water contained in a calorimeter of mass 50 g at 32 °C such that the final temperature is 5 °C. Specific heat capacity of calorimeter = 0.4 J g-1 °C-1, Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1°C-1, latent heat capacity of ice = 330 J g-1.
50 g of metal piece at 27°C requires 2400 J of heat energy so as to attain a temperature of 327°C . Calculate the specific heat capacity of the metal.
Heat energy is supplied at a constant rate to 100g of ice at 0 °C. The ice is converted into water at 0° C in 2 minutes. How much time will be required to raise the temperature of water from 0 °C to 20 °C? [Given: sp. heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 °C-1, sp. latent heat of ice = 336 J g-1].
A solid metal weighing 150 g melts at its melting point of 800 °C by providing heat at the rate of 100 W. The time taken for it to completely melt at the same temperature is 4 min. What is the specific latent heat of fusion of the metal?
Discuss the role of high specific heat capacity of water with reference to climate in coastal areas.
Water property of water makes it an effective coolant?
Give one example where high specific heat capacity of water is used as heat reservoir ?
An electric heater of power 600 W raises the temperature of 4.0 kg of a liquid from 10.0℃ to 15.0℃ in100 s. Calculate:
- the heat capacity of 4.0 kg of liquid,
- the specific heat capacity of the liquid.
How will global warming disturb the ecological balance?
The product of mass and specific heat is known as ..........
Define heat capacity and state its units.
State the condition for the flow of heat energy from one body to another.
Write the approximate values of the specific latent heat of fusion of ice.
Explain, Why is it advisabile to pour cold water over burns, caused on human body, by hot solids?
1 kg of water freezes to form ice at 0°C. What amount of heat is withdrawn?
How much heat energy is released when 5 g of water at 20° C changes to ice at 0° C?
[Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 ° C-1 Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1]
A piece of iron of mass 2.0 kg has a thermal capacity of 966 J/°C. What is its specific heat capacity in S.I. units?
Solve the following problem.
Specific latent heat of vaporization of water is 2.26 × 106 J/kg. Calculate the energy needed to change 5.0 g of water into steam at 100 ºC.
From the options given below the specific heat of _______ is maximum.
Write the name.
The amount of heat absorbed at constant temperature by unit mass of a liquid to convert into gaseous phase.
Consider the statement given below and choose the correct option.
Assertion: Radiation is a form of heat transfer which takes place only in vacuum.
Reason: The thermal energy is transferred from one part of a substance to another part without the actual movement of the atoms or molecules.
The value of 'γ' for a gas is given as `gamma = 1 + 2/"f"`, where 'f ' is the number of degrees of freedom of freedom of a molecule of a gas. What is the ratio of `gamma_"monoatonic"//gamma_"diatomic"`?
Diatomic gas consists of rigid gas molecules
For a gas `"R"/"C"_"v" = 0.4,` where 'R' is the universal gas constant and 'Cv' is molar specific heat at constant volume. The gas is made up of molecules which are ______.
An office room contains about 4000 moles of air. The change in the internal energy of this much air when it is cooled from 34° C to 19° C at a constant pressure of 1.0 atm is (Use `gamma_"air"` = 1.4 and Universal gas constant = 8.314 J / mol K) ____________.
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for 200 g of water. The heat is extracted at the rate of 100 Js-1. Answer the questions that follow:
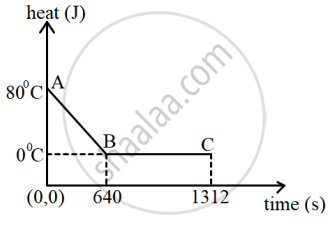
- Calculate specific heat capacity of water.
- Heat released in the region BC.
Two metals A and B have specific heat capacities in the ratio 2:3. If they are supplied same amount of heat then
Which metal piece will have greater mass if the rise in temperature is the same for both metals?
Specific heat capacity C = ______.
