Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe, in brief, the changes the uterus undergoes
(i) to receive the zygote.
(ii) if zygote is not formed
उत्तर १
(i) If the uterus receives the zygote, the female becomes pregnant. The embryonic development of the zygote starts immediately. The embryo moves down into the uterus forming a thick and soft lining of blood vessels around itself. This process is called implantation. After implantation, a special tissue develops between the uterine wall and the embryo called placenta, where the exchange of nutrients, oxygen and waste products takes place.
(ii) If the egg released by the ovary is not fertilized and the zygote is not formed, then the thick lining of the uterus breaks down and comes out through the vagina in the form of blood and mucous. This is called menstruation.
उत्तर २
(i)The uterus prepares itself every month to receive a fertilised egg/zygote. The inner uterus lining (endometrium) becomes thick and is supplied with blood to nourish the embryo.
(ii) If the egg is not fertilised, then the uterus lining is not required. Hence, it breaks down and gets released in the form of blood and mucous through the vagina. This process lasts for 2–8 days. This cycle occurs every month and is known as menstruation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State its functions in case of a pregnant human female.
Give scientific reasons: When an ovum gets fertilized, menstrual cycle stops temporarily in a woman.
What is the name of the process in which thickened uterus lining alongwith blood vessels is removed from the body of a human female through vaginal bleeding?
Which of the following is not a sexually transmitted disease?
(a) gonorrhoea
(b) hepatitis
(c) syphilis
(d) AIDS
Write two examples of sexually transmitted diseases caused by bacteri.
Trace the path of sperms from where they are produced in human body to the exterior.
Describe in brief the role of ureter in human male reproductive system.
Give the names.
Any two sexual diseases.
Label the folowing diagram
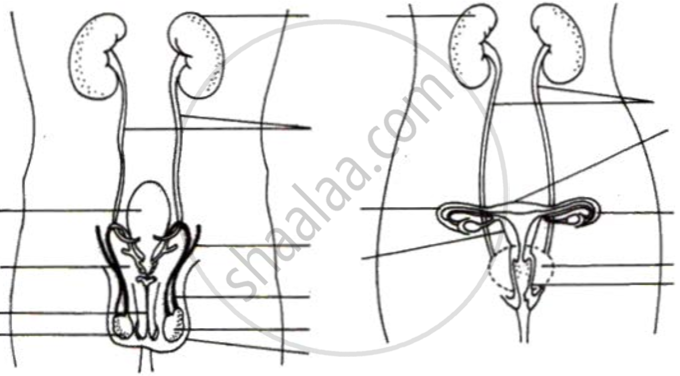
Differentiate
Urinogenital system and Urinary system.
