Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the development of dicot embryo in flowering plants.
दीर्घउत्तर
उत्तर
Development of dicot embryo:
- The zygote divides to form a two-celled proembryo.
- The larger cell towards the micropyle is called basal or suspensor initial cell and the smaller cell towards chalaza is called terminal or embryonal initial cell.
- The suspensor cell divides transversely in one plane to produce a filamentous suspensor of 6-10 cells.
- The first cell of the suspensor towards the micropylar end becomes swollen and functions as a haustorium.
- The lowermost cell of suspensor is known as hypophysis.
- The suspensor helps in pushing the embryo into the endosperm.
- The embryonal initial undergoes three successive mitotic divisions to form octant.
- The planes of divisions are at right angles to each other.
- The lower tier of four cells of octant give rise to hypocotyl and radicle whereas four cells of upper-tier form the plumule and the one or two cotyledons.
- The hypophysis by further division gives rise to the part of the radicle and root cap.
- Subsequently, the cells in the upper tier of octant divide into several planes so as to become heart-shaped which then forms two lateral cotyledons and a terminal plumule.
- Further enlargement of hypocotyl and cotyledons result in a curvature of the embryo and it appears horse-shoe shaped.
shaalaa.com
क्या इस प्रश्न या उत्तर में कोई त्रुटि है?
संबंधित प्रश्न
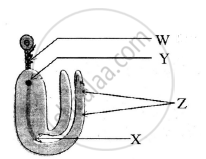
Name the parts W, X, Y and Z from the following figure:
From the following identify the non endospermic seeds.
Which of the following is the role of suspensor?
In angiosperms, during development of embryo, the suspensor cells develop from which of the following?
Father of Indian embryology is ______.
Coleoptile and coleorhiza are the protective sheaths covering ______ and ______ respectively.
______ is not an endospermic seed.
In the embryos of a typical dicot and a grass, true homologous structures are ______.
Name the common function that cotyledons and nucellus perform.
List the components of embryo sac and mention their fate after fertilization.
