Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the process of spermatogenesis with the help of diagram.
उत्तर

Spermatogenesis is the process of formation of the male gamete (sperm) or spermatozoa from the germinal epithelium of the testis. At the onset of puberty, the hypothalamus begins secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). GnRH initiates a significant increase in the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) which in turn induces spermatogenesis. Each seminiferous tubule is lined by a single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells called the germinal epithelium. The cells of germinal epithelium undergo spermatogenesis to produce sperms.
The process of spermatogenesis involves three phases:
- Multiplication phase: The primordial germ cells (2n) of the seminiferous tubules undergo repeated mitotic divisions to produce a large number of spermatogonia (2n). Each spermatogonium is diploid and with 46 chromosomes.
- Growth phase: Some of the spermatogonia stop dividing and grow in size to develop into primary spermatocytes (2n) due to the accumulation of food.
- Maturation phase: It involves meiotic or reduction division. The spermatocyte undergoes the first phase of meiotic division (meiosis I) leading to the formation of two haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes (n) having 23 chromosomes each. The secondary spermatocyte undergoes the second phase of meiotic division (meiosis II) to produce four haploid spermatids. The spermatid is non-motile and non-functional. It gets transformed into functional spermatozoa by the process called spermiogenesis. Changes during spermiogenesis: During this process of change, the spermatids remain held to each other and to the Sertoli cells by cytoplasmic bridges. The sperm heads remain attached to the Sertoli cells with their tails hanging in the lumen of the seminiferous tubule. During spermiogenesis, the length of the spermatid increases. Centrioles are rearranged as primary and distal centrioles. Mitochondria become spirally coiled and acrosome is formed from the Golgi complex.
संबंधित प्रश्न
The process of release of the ovum from a mature follicle is called __________.
Fill in the blank.
---------- type of reproduction occurs without fusion of gametes.
In angiosperms, the pollen germinates to produce a pollen tube that carries two gametes. What is the purpose of carrying two gametes when a single gamete can fertilize the egg?
If one pollen grain produces two male gametes, how many pollen grains are needed to fertilize 10 ovules?
The following is the illustration of the sequence of ovarian events (a-i) in a human female.
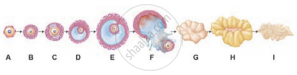
Identify the figure that illustrates ovulation and mention the stage of oogenesis it represents.
Which of the following contains a fluid filled cavity called antrum?
Corona radia is made up of ______.
The prostate gland and seminal vehicle perform the function of ______.
Read the following and answer from given below:
Oogenesis is the process of the formation of an ovum in the ovaries. It consists of three phases: multiplication, growth, and maturation. Oogenesis is controlled by hormones GnRH, LH, FSH. GnRH secreted by the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to secrete LH and FSH.
Which cell division is involved in the formation of secondary oocytes?
In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
