Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the structure of the cerebrum. Add a note on its function.
उत्तर
Structure of the cerebrum:-
- It is the largest portion of the brain and constitutes about 80–85% of the weight of the brain.
- It is divided into two cerebral hemispheres by a median longitudinal fissure.
- The cerebral hemispheres are connected to each other by a thick band of transverse nerve fibers called the corpus callosum.
- A cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is present in each hemisphere. It is called the lateral ventricle.
- The outer surface of the cerebral hemisphere is called the cerebral cortex.
- The cortex contains cell bodies of the neuron and is greyish; hence, it is called grey matter.
- The grey matter has many folds (i.e. gyri) and grooves (i.e. sulci). They increase the surface area to accommodate more nerve cells.
- A higher number of convolutions lead to greater intelligence.
- The inner surface of the cerebral hemisphere is called the cerebral medulla.
- The medulla consists of axons of nerve fibers and is called white matter.
- Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four lobes—frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe.
- The frontal and occipital lobes are separated by a central sulcus; the parietal and temporal lobes are separated by a lateral sulcus, while the parietal and occipital lobes are separated by a parieto-occipital sulcus.

Functions of the cerebrum:-
- The cerebrum determines intelligence in animals.
- It is also the center of learning and memorising in the brain.
Functional areas of the cerebrum:-
- Frontal lobe:- It consists of the motor area which controls voluntary activities. Broca’s area is the motor speech area which translates thoughts into speech and controls the movements of the tongue, lips, and vocal cords. The association area related to intelligence, memory, judgment, and problem-solving ability is found in the frontal lobe.
- Parietal lobe:- The general sensory area associated with the sensation of temperature, touch, pressure, pain, and speech is located on the post-central gyrus of the parietal lobe.
- Temporal lobe:- The areas concerned with the sense of taste, sense of hearing, and sense of smell are located on the temporal lobe.
- Occipital lobe:- It carries the sensory visual area concerned with the sense of vision and the association visual area for perception, analysis, and storage of information obtained by sight.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statement:
Spinal cord is an extention of:
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word :
The part of brain where the respiratory centre is located is _______________.
The below diagram represents the human brain as seen in an external view. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
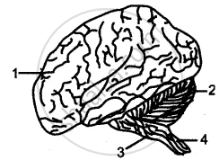
(i) Name the parts labeled 1, 2, 3, and 4.
(ii) Mention the difference in the arrangement of the nerve cells in the parts marked ‘1’ and ‘4’.
(iii) What is the main function of the parts marked ‘3’ and ‘4’?
(iv) Name the sheet of nerve fibers that connect the two halves of the part labeled ‘1’.
Functional unit of brain is ______
The part of the human brain which acts as a relay center is ______.
All are functions ofvasopressin, EXCEPT
Identify the parts of the hind brain.
Medulla oblongata controls involuntary vital activity such as ______
Assertion: Brain is a delicate organ which is protected from injury.
Reason: The bony box protects the brain from any shock.
Kathak is an Indian classical dance which involves a lot of spinning by the dancers. The learners of this dance experience dizziness in the beginning while spinning.

Mention the nerve that carries the impulse for dizziness to the brain.
