Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
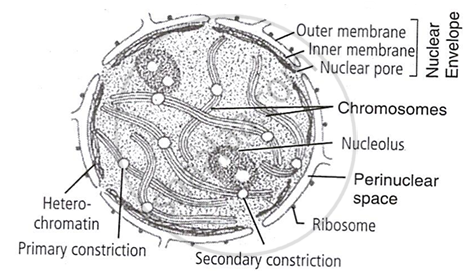
Describe the structure of the following with the help of labelled diagram.
Nucleus
उत्तर
The nucleus is a double membrane-bound principle cell organelle that contains all genetic information for controlling cellular metabolism and transmitting genetic information.
Nucleus is differentiated into following four parts:
- Nuclear envelope: A double membrane bound envelope surrounds the nucleus and separates the latter from the cytoplasm.
- Nucleoplasm: It is clear, non-staining, fluid material present in the nucleus, which contains raw materials (nucleotides), enzymes (DNA/RNA polymerases) and metal ions for the synthesis of RNAs and DNA. The nuclear matrix or the nucleoplasm, is composed of nucleolus and chromatin.
- Nucleolus: It is a naked, round and slightly irregular structure, which is attached to the chromatin at a specific region. It is a site for active ribosomal RNA synthesis.
- Chromatin: It has the ability to get stained with certain basic dyes. It is known to be the hereditary DNA protein fibrillar complex. The chromatin fibres are distributed throughout the nucleoplasm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are nuclear pores?
What is a centromere?
How does the position of centromere form the basis of classification of chromosomes. Support your answer with a diagram showing the position of centromere on different types of chromosomes.
In a cell that is not dividing, the chromosomes are visible as a tangle of fine threads called
Chromosome having centromere in its middle is
When the centromere is situated in the middle of two equal arms of chromosomes, the chromosome is referred to as ______
Match List - I with List - II.
| List - I | List - II | ||
| (a) | Cristae | (i) | Primary constriction in chromosome |
| (b) | Thylakoids | (ii) | Disc-shaped sacs in Golgi apparatus |
| (c) | Centromere | (iii) | Infoldings in mitochondria |
| (d) | Cisternae | (iv) | Flattened membranous sacs in the stroma of plastids |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
A common characteristic feature of plant sieve tube cells and most of mammalian erythrocytes is ______.
What is refer-ed to as satellite chromosome?
Discuss briefly the role of nucleolus in the cells actively involved in protein synthesis.
What are histones? What are their functions?
Explain the functions of the nuclear pores.
