Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Differentiate between the following:
Binary fission and budding
उत्तर
Binary fission
- It is the kind of asexual reproduction in which a parent cell splits into two new organisms of same size.
- Mostly unicellular organisms like bacteria show binary fission
- Parent cell and newly formed cells are similar in size.
- Cytoplasm of parent cell divides equally.
- It is a natural process and can not be done artificially.

Budding
- It is the kind of asexual reproduction in which a parent cell forms an out- growth as a bud and this but detaches to form a new individual multicellular.
- Multicellular organisms like yeast reproduce using budding.
- Parent cell is larger than the newly formed bud.
- Cytoplasm divides unequally parent cell has more cytoplasm than bud.
- It is a type of vegetative propagation and can be done artificially.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Differentiate between 'stem tuber' and 'tuberous root'.
Vegetative propagation takes place with the help of leaves in _________ plant.
…………. is a mode of asexual reproduction.
(a) Cloning
(b) Budding
(c) Pollination
(d) Germination
Explain the term “Regeneration” as used in relation to reproduction of organisms
Explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
External fertilisation takes place in frogs.
Fertilisation is necessary even in asexual reproduction.
Define asexual reproduction.
Draw in sequence (showing the four stages), the process of binary fission in Amoeba.
What is meant by the term 'artificial propagation of plants'?
Name two fruit trees which are usually propagated by grafting method.
A worm X found in freshwater and slow-moving streams has been accidently cut into three pieces. It was observed that in due course of time, each cut piece of the worm develops to become a complete worm by growing all the missing parts.
(a) Name the worm X which can exhibit this phenomenon of making complete worm from its cut body parts.
(b) Name another organism Y which possesses the same characteristic of growing fully from its cut body parts.
(c) What is the name of this process in which a complete organism is formed from its cut body part.
(d) State whether X and Y are unicellular and/or multicellular organisms.
(e) Can a dog be produced completely form its cut body part (say, a cut tail) just like organisms X and Y? Why?
When a broken piece of the stem of a plant X is planted in the soil, a new plant grows from it in a week's time. The leaves of plant X also have many small entities Y in their margins which can fall to the ground alone or alongwith leaves and grow into new plants.
(a) Name a plant which X could be.
(b) What are the entities Y present on the leaves of X known as?
(c) Name a plant other than X which can be reproduced from its leaves.
(d) Name a common plant grown in many homes which can be propagated from its broken stems like plant X.
(e) Name a kind of dormant organs present in dry stems of old grass plants lying in the fields which get activated and produce green grass plants after the rains.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The process of fusion of gametes is called .............
Multiple choice question. Tick (✓) the correct choice:
Reproduction or propagation by stem is common in
- begonia
- potato
- sweet potato
- Bryophyllum
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F):
Cutting and grafting are natural means of reproduction.
Find the odd-one out, giving reason.
Cutting, grafting, layering, binary fission.
Mention the common method of reproduction in Potato.
Mention the common method of reproduction in Strawberry.
Describe the various methods of vegetative reproduction.
Choose the correct statement(s) on budding in yeast from the following :
I. A parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells and here the parent identity is lost.
II. In this the elongated nucleus divides to form two or more daughter nuclei.
III. A bud arises from a particular region on a parent body.
IV. After detaching from the parent body the bud grows into a new independent individual.
(A) I only
(B) III only
(C) II and III only
(D) III and IV only
A student after observing a slide showing different stages of binary fission in Amoeba draws the following diagrams. However these diagrams are not in proper sequence: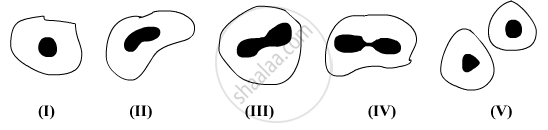
The correct sequence is:
(A) I, V, IV, III, II
(B) I, III, IV, V, II
(C) I, V, III, IV, II
(D) I, IV, V, III, II
A student after viewing a prepared slide illustrates the budding in yeast in the following order which is not correct:

(A) b, c, d, e, a
(B) b, e, d, c, a
(C) b, d, e, c, a
(D) b, d, c, e, a
In which of the following figures is budding not shown?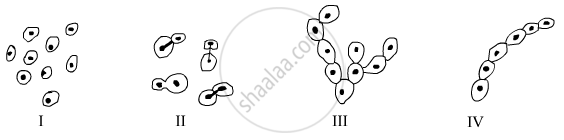
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
What is meant by vegetative propagation? Name the vegetative parts through which Potato and Bryophyllum reproduce.
Draw a labelled diagram in proper sequence to show budding in hydra.
Give the name of the plant that reproduces vegetatively by: Stem-cutting
Give the name of the plant that reproduces vegetatively by: Underground stem
How is plant hybridisation carried out?
How is vegetative propagation economically important?
The plants produced as a result of vegetative reproduction are
Vegetative propagation by leaves takes place in ______.
Asexual reproduction is also known as ______.
Budding, in hydra, is a form of ______.
The ability of a cell to divide into several cells during reproduction in Plasmodium is called ______
When you keep food items like bread and fruits outside for a long time, especially during the rainy season, you will observe a cottony growth on them.
What is this growth called?
Vegetative reproduction of Agave occurs through ______.
