Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
Respiratory quotient (RQ): It is the ratio of CO2 output to O2 uptake. It is denoted by R.
R = Rate of CO2 output/Rate of O2 uptake
RQ for carbohydrate = 1.00
RQ for fat = 0.70
RQ for protein = 0.85
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
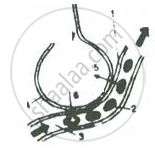
Given alongside is a diagrammatic sketch of a kind of part in human lungs.
Name the parts numbered 1-4
The volume of air in the lungs and the rate at which it is exchanged during inspiration and expiration was measured.
The following diagram shows a group of the lung volumes and capacities.
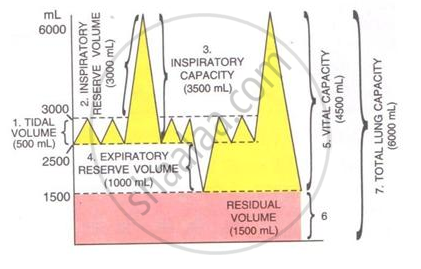
Study the diagram carefully and explain briefly the following :
Residual volume (RV)
Name the following:
Respiratory process in which oxygen is not utilized.
What happens to the energy liberated during respiration?
What do you understand by inhalation and exhalation? How are they different from each other?
What do you understand by the term respiratory diseases? Name any three common respiratory diseases.
Fill in the blanks.
The respiration is of two types _________ and _________
Write true or false for the following statement. Rewrite the false statement correctly.
The oxidation of food to release energy and water is called breathing.
Write true or false for the following statement. Rewrite the false statement correctly.
The microscopic air sacs present in the lungs are called bronchi.
What is the full form of ATP?
Name the following:
Body cavity in which lungs are situated.
Answer the following question.
Give an account on the tracheal system of cockroach.
Alveoli provide the surface area for exchange of ______.
What is respiration?
Identify the CORRECT term for the following description:
The maximum amount of air that can be breathed out after a maximum inspiration.
In which of the following form/way approximately seventy percent of carbon dioxide absorbed by the blood will be transported to the lungs?
______ of nasal chamber warms the air and makes it moist.
For completion of respiration process, write the given steps in sequential manner
- Diffusion of gases (O2 and CO2) across alveolar membrane.
- Transport of gases by blood.
- Utilisation of O2 by the cells for catabolic reactions and resultant release of CO2.
- Pulmonary ventilation by which atmospheric air is drawn in and CO2 rich alveolar air is released out.
- Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and tissues.
Name the lymphoid organ present in the human pharynx.
