Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Discuss the important features of the law of gravitation.
उत्तर
1. As the distance between two masses increases, the strength of the force tends to decrease because of inverse dependence on r2. Physically it implies that the planet Uranus experiences less |F| gravitational force from the Sun than the Earth since Uranus is at a larger distance from the Sun compared to the Earth.
2. The gravitational forces between two particles always constitute an action-reaction pair. It implies that the gravitational force exerted by the Sim on the Earth is always towards the Sun. The reaction force is exerted by the Earth on the Sun. The direction of this reaction force is towards Earth.
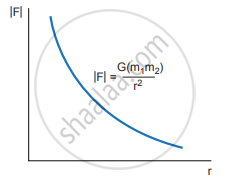
Variation of gravitational force with distance
3. The torque experienced by the Earth due to the gravitational force of the Sun is given by
`vecτ = vec"r" xx vec"F" = vec"r" xx (-("GM"_"S""M"_"E")/"r"^2 hat"r") = 0`
Since `vec"r" = "r", hat"r", (hat"r" xx hat"r") = 0`
So `vecτ = ("d" vec"L")/"dt" = 0`
It implies that angular momentum `vec"L"` is a constant vector.
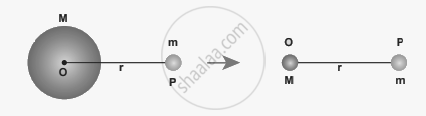

Hollow sphere of mass
4. The expression `vec"F" = -("GM"_1"M"_2)/"r"^2 hat"r""` has one inherent assumption that both M1, and M2 are treated as point masses. When it is said that Earth orbits around the Sun due to Sun’s gravitational force, we assumed Earth and Sun to be point masses.
5. Point masses hold even for a small distance.
6. There is also another interesting result. Consider a hollow sphere of mass M. If we place another object of mass ‘m’ inside this hollow sphere the force experienced by this mass ‘m’ will be zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The linear momentum and position vector of the planet is perpendicular to each other at _________.
According to Kepler’s second law, the radial vector to a planet from the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. This law is a consequence of ___________.
State Kepler’s three laws.
Explain how Newton verified his law of gravitation.
Assume that you are in another solar system and provided with the set of data given below consisting of the planets’ semi-major axes and time periods. Can you infer the relation connecting semi-major axis and time period?
| Planet (imaginary) | Time period (T) (in year) | Semi-major axis (a) (in AU) |
| Kurinji | 2 | 8 |
| Mullai | 3 | 18 |
| Marutham | 4 | 32 |
| Neithal | 5 | 50 |
| Paalai | 6 | 72 |
If the masses and mutual distance between the two objects are doubled, what is the change in the gravitational force between them?
If the angular momentum of a planet is given by `vec"L" = 5"t"^2hat"i" - 6"t"hat"j" + 3hat"k"`. What is the torque experienced by the planet? Will the torque be in the same direction as that of the angular momentum?
The escape velocity of a body depends upon mass as ______
The escape velocity of a body on a planet 'A' is 12 kms–1. The escape velocity of the body on another planet 'B', whose density is four times and radius is half of the planet 'A', is ______.
The time period of a satellite revolving around the earth in a given orbit is 7 hours. If the radius of the orbit is increased to three times its previous value, then the approximate new time period of the satellite will be ______.
