Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Distinguish Between Internal or anatomical difference between monocots and dicots.
उत्तर
| Monocots | Dicots | |
| 1. | The stem shows scattered vascular bundles. | The stem shows vascular bundles that are arranged in ring-like manner. |
| 2. | Vascular bundles are conjoint collateral closed without cambium in the stem. | Vascular bundles are conjoint collateral and without cambium in the stem. open with fascicular cambium. |
| 3. | The root shows polyarch condition with broad pith. | The root shows tetrach and hexarch condition with narrow pith. |
| 4. | In stem, epidermis is without trichomes and hypodermis which is of sclerenchyma. | In stem, epidermis is with trichomes and hypodermis which is of collenchyma. |
| 5. | Guard cells of stomata are dumb-bell shaped. | Guard cells of stomata are kidney-shaped. |
| 6. | The leaf shows stomata on both upper and lower epidermis. Amphistomatic leaf. | The leaf shows stomata which are mainly on the lower epidermis. Hypostermatic leaf. |
| 7. | The leaf is isobilateral with undifferentiated mesophyll. | The leaf is dorsiventral with mesophyll differentiated into palisade and spongy. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Explain different types of elements present in phloem.
What is the differences between collenchyma and sclerenchyma?
Study the diagram given below and then answer the question that follows:
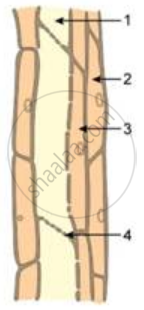
Where is this tissue likely to be found in the plant?
Define the following:
Permanent tissue
The question has four answers. Choose the correct answer:
A component of xylem is
The question has four answers. Choose the correct answer:
Phloem parenchyma, sclerenchyma, sieve tubes, and companion cells are found in
Explain sclereids with their types.
Differentiate fibers from sclereids.
The cells or tissues of plants which have lost the power of division are called
