Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a neat labelled diagram for a particle moving in a circular path with a constant speed. In you diagram show the direction of velocity at any instant.
उत्तर
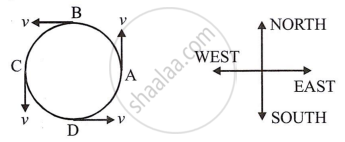
Direction of velocity in uniform circular motion
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a particle performing uniform circular motion `vecv=vecomegaxxvecr`obtain an expression for linear acceleration of the particle performing non-uniform circular motion.
Give an example of motion in which speed remains uniform, but the velocity changes.
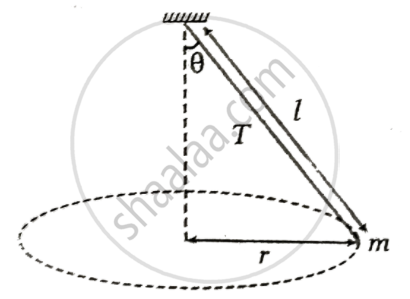
A ball of mass 'm' is attached to the free end of an inextensible string of length 'l'. Let 'T' be the tension in the string. The ball is moving in horizontal circular path about the vertical axis. The angular velocity of the ball at any particular instant will be ______.
A string of length 'l' fixed at one end carries a mass 'm' at the other end. The string makes `3/pi` revolutions/second around the vertical axis through the fixed end as shown in figure. The tension 'T' in the string is ______.
The angular speed of the minute hand of a clock in degrees per second is ______.
The motion of the bus is ______ motion.
A flywheel at rest is to reach an angular velocity of 24 rad/s in 8 second with constant angular acceleration. The total angle turned through during this interval is ______.
If a body is moving in a circle of radius r with a constant speed v, its angular velocity is ______.
For a particle performing uniform circular motion, choose the correct statement(s) from the following:
- Magnitude of particle velocity (speed) remains constant.
- Particle velocity remains directed perpendicular to radius vector.
- Direction of acceleration keeps changing as particle moves.
- Angular momentum is constant in magnitude but direction keeps changing.
A particle is performing a uniform circular motion along a circle of radius R. In half the period of revolution, its displacement and distance covered are respectively.
