Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
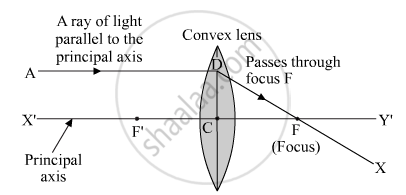
Draw the given diagram in your answer book and complete it for the path of a ray of light after passing through the lens.
उत्तर
The ray will pass through the focus after refraction since it is parallel to the principle axis. See the diagram given below.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
If the focal length of a spherical mirror is 12.5 cm, its radius of curvature will be:
(a) 25 cm
(b) 15 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 35 cm
If you want to see an enlarged image of your face, state whether you will use a concave mirror or a convex mirror?
Which mirror always produces a virtual, erect and diminished image of an object?
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image in a convex-mirror when the object is at infinity. Mark clearly the pole and focus of the mirror in the diagram.
Two big mirrors A and B are fitted side by side on a wall. A man is standing at such a distance from the wall that he can see the erect image of his face in both the mirrors. When the man starts walking towards the mirrors, he find that the size of his face in mirror A goes on increasing but that in mirror B remains the same.
(a) mirror A is concave and mirror B is convex
(b) mirror A is plane and mirror B is concave
(c) mirror A is concave and mirror B is plane
(d) mirror A is convex and mirror B is concave
A convex mirror used as a rear-view mirror in a car has a radius of curvature of 3 m. If a bus is located at a distance of 5 m from this mirror, find the position of image. What is the nature of the image?
Nature of the images formed by a convex mirror is _______.
An object at a distance of +15 cm is slowly moved towards the pole of a convex mirror. The image will get ______.
Why a convex mirror is preferred for rearview mirrors in cars?
