Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a labeled diagram of a full wave rectifier circuit. State its working principle. Show the input-output waveforms ?
उत्तर
To get an output voltage for both half cycles of the input signal, we use full wave rectifiers. The commonly used full wave rectifier circuits are center-tap rectifier and bridge rectifier. The figure below shows the center-tap rectifier circuit.

Now consider the circuit. The P-side of the diodes D1 and D2 are connected to the secondary terminals of the transformer. The N-sides of the diodes are connected together. The load is connected between this point and the midpoint of the transformer. When the input signal to diode D1 is positive, it conducts and load current flows. During this time, the input to diode D2 is negative with respect to the midpoint. During the negative half cycle of the input signal, the voltage at D1 is negative and that at D2 is positive. So D2 conducts during this time period. Thus we get output voltage during both the half cycles. As the full wave rectifier rectifies both the half cycles, it is more efficient than the half wave rectifier. The waveforms are given below:

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A power transmission line feeds input power at 2200 V to a step-down transformer with its primary windings having 300 turns. Find the number of turns in the secondary to get the power output at 220 V.
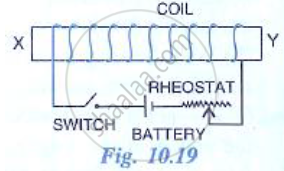
The adjacent diagram shows a coil would around a soft iron bar XY. (a) State the polarity at the end X and Y as the switch is pressed. (b) Suggest one way increasing the strength of electromagnet so formed.
(i) Draw a clear labelled diagram of an electric bell.
(ii) Explain in brief, its working.
(iii) What material is used for the core of an electric bell? State the reason.
The primary of a transformer has 40 turns and works on 100 V and 100 W. Find a number of turns in the secondary to step up the voltage to 400 V. Also calculate the current in the secondary and primary.
A transformer having efficiency of 80% is working on 200 V and 6 kW power supply. If the current in the secondary coil is 6 A, the voltage across the secondary coil and the current in the primary coil respectively are ____________.
Read the following paragraph and answer the question:

Long distance power transmissions
The large-scale transmission and distribution of electrical energy over long distances is done with the use of transformers. The voltage output of the generator is stepped up. It is then transmitted over long distances to an area sub-station near the consumers. There the voltage is stepped down. It is further stepped down at distributing sub-stations and utility poles before a power supply of 240 V reaches our homes.
We need to step-up the voltage for power transmission, so that ______.
A transformer is essentially an a.c. device. It cannot work on d.c. It changes alternating voltages or currents. It does not affect the frequency of a.c. It is based on the phenomenon of mutual induction. A transformer essentially consists of two coils of insulated copper wire having different numbers of turns and wound on the same soft iron core.
The number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of an ideal transformer is 2000 and 50 respectively. The primary coil is connected to a main supply of 120 V and secondary coil is connected to a bulb of resistance 0.6 Ω.
Power in primary coil is ______.
Define a Transformer.
The primary coil of a transformer has 800 turns and the secondary coil has 8 turns. It is connected to a 220 V ac supply. What will be the output voltage?
The line that draws power supply to your house from street has ______.
- zero average current.
- 220 V average voltage.
- voltage and current out of phase by 90°.
- voltage and current possibly differing in phase `phi` such that `|phi| < pi/2`.
