Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
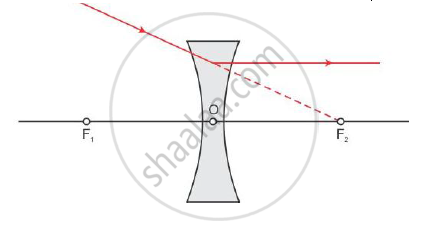
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the refracted ray in each of the following cases:-
A ray of light incident on a concave lens is
(i) passing through its optical centre.
(ii) parallel to its principal axis.
(iii) directed towards its principal focus.
उत्तर
(i) A ray of light passing through the optical centre of the concave lens will emerge without any deviation.

(ii) A ray of light parallel to the principal axis, after refraction from a concave lens, appears to diverge from the principal focus on the same side of the lens.

(iii) A ray of light directed towards the principal focus of a concave lens, becomes parallel to its principal axis after refraction through the lens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State two positions in which a concave mirror produces a magnified image of a given object. List two differences between the two images.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror.
(i) Write the type of mirror in this case.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror ?
(iii) What is the nature of the image formed ?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 25 cm. At which of the following distance should a person hold his face from this concave mirror so that it may act as a shaving mirror?
(a) 45 cm
(b) 20 cm
(c) 25 cm
(d) 30 cm
Give reason for your choice.
Describe the nature of image formed when the object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
The diagram shows a dish antenna which is used to receive television signals from a satellite. The antenna (signal detector) is fixed in front of the curved dish.
Figure
(a) What is the purpose of the dish?
(b) Should it be concave or convex?
(c) Where should the antenna be positioned to receive the strongest possible signals?
(d) Explain what change you would expect in the signals if a larger dish was used.
If the radius of curvature of a concave mirror is 20 cm, its focal length is:
Draw the ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
List four characteristics of the image formed by a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm when the object is placed in front of it at a distance of 20 cm from its pole.
Match the following.
| Convex mirror | Radio telescopes |
| Parobolic mirror | Rear – view mirror |
| Snell’s law | Kaleidoscope |
| Dispersion of light | sin i/sin r =μ |
| Refractive index | Rainbow |
